Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
Why Does My WiFi Keep Disconnecting? Causes and Solutions
This guide covers the most common causes of WiFi disconnects and practical fixes you can try right away — with NetSpot as a tool to help you identify what’s actually happening.
Common Reasons Why Internet Keeps Disconnecting
Random connection drops usually have fairly trivial causes. If your WiFi connection occasionally disappears or becomes unstable, the root cause usually falls into one of several categories. Here’s a breakdown of the most frequent reasons for network interruptions — and how they can be addressed.
- Weak or inconsistent signal: Signal strength is one of the biggest factors in WiFi stability. If your router is located too far from key devices, or if there are thick walls and obstructions between them, coverage can become patchy. Some routers also struggle to reach across large homes or multiple floors. Our separate guide on improving WiFi signal strength explores this issue in more detail.
- Network congestion: A busy network can start acting like it’s unreliable: devices reconnect, latency spikes, and things feel inconsistent. This happens more often with older routers or when several devices are streaming, gaming, backing up photos, and doing updates at the same time.
- Interference from nearby equipment: WiFi shares its frequency bands with a variety of other electronics. Microwaves, Bluetooth accessories, and even neighboring routers operating on overlapping channels can introduce interference, leading to unstable performance — especially on the crowded 2.4 GHz band.
- ISP-related outages: Sometimes the problem lies outside your network. Your provider may be experiencing temporary outages, maintenance, or regional issues that will affect your signal quality regardless of your home network configuration.
- Router limitations or hardware faults: Overheating, aging hardware, or outdated firmware can all affect router performance. In some cases, the router may still appear to be working, but quietly reboot or drop certain clients due to internal faults or memory leaks.
- Device-side problems: The WiFi adapter inside your computer or mobile device plays a crucial role. Corrupted drivers, power-saving settings, or hardware issues can cause only certain devices to lose connection — even if the router is working fine for others.
- Power instability: Non-obvious factors such as a weak power supply, a loose connector, or a faulty surge protector can also cause a router to reboot quickly. If you see the lights flashing or the router "resumes operation" after a minute, it's time to check the power supply.
- Security threats or malware: Routers can be infected with malware, such as the infamous ZuoRAT malware, which infected routers made by Cisco, Netgear, Asus, and DrayTek and caused serious connectivity issues as it allowed attackers to gain access to devices on the same network.
Note: In some cases, a slow internet connection might be mistaken for Wi-Fi disconnections. If you suspect your internet speed is the issue, visit our why is my Internet so slow page for helpful tips and solutions.
How to Troubleshoot and Fix Disconnecting Internet
Knowing the common causes of why your WiFi keeps disconnecting is just the first step towards solving the problem. Determining which specific issue is responsible for your connectivity woes is where the challenge truly begins.
However, this task becomes much more manageable when you approach the troubleshooting process methodically and use a capable WiFi analytics software, like NetSpot, to provide you with the data you need.
1. Start With the Basics
We recommend you start by restarting your router. The classic "turn it off and on again" fix works surprisingly often as it can clear temporary errors and refresh connections. While you're at it, you might as well plug your router into a different outlet (preferably using a different adapter) to rule out power issues.
2. Use a WiFi Analyzer App to Scan Your WiFi
When basic troubleshooting steps don't resolve the issue, it's time to employ a more advanced tool like NetSpot, a highly capable WiFi analyzer app. NetSpot can help diagnose why your internet connection keeps dropping and reconnecting by providing valuable insights into your WiFi environment.
NetSpot's Inspector Mode collects every detail about surrounding WiFi networks and presents wireless data as an interactive table.
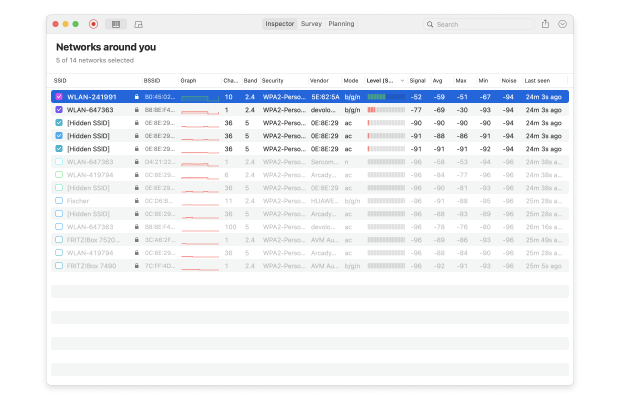
With it, you can easily see, for example, how many networks there are around you and which WiFi channels they're using. If your own network happens to be broadcasting on one of the more cluttered channels, then it's likely that interference is the cause of your issues, and switching to a different channel should help.
To use Inspector Mode, follow these brief instructions:
Launch the app and make sure Inspector mode is selected.
Wait a few seconds until NetSpot gathers data about available networks.
To determine if your WiFi signal is strong enough to be stable and reliable, you can use NetSpot's Survey Mode to conduct in-depth network analysis whose outcomes are easy-to-understand color-coded heatmaps that visually identify problem areas in your network.
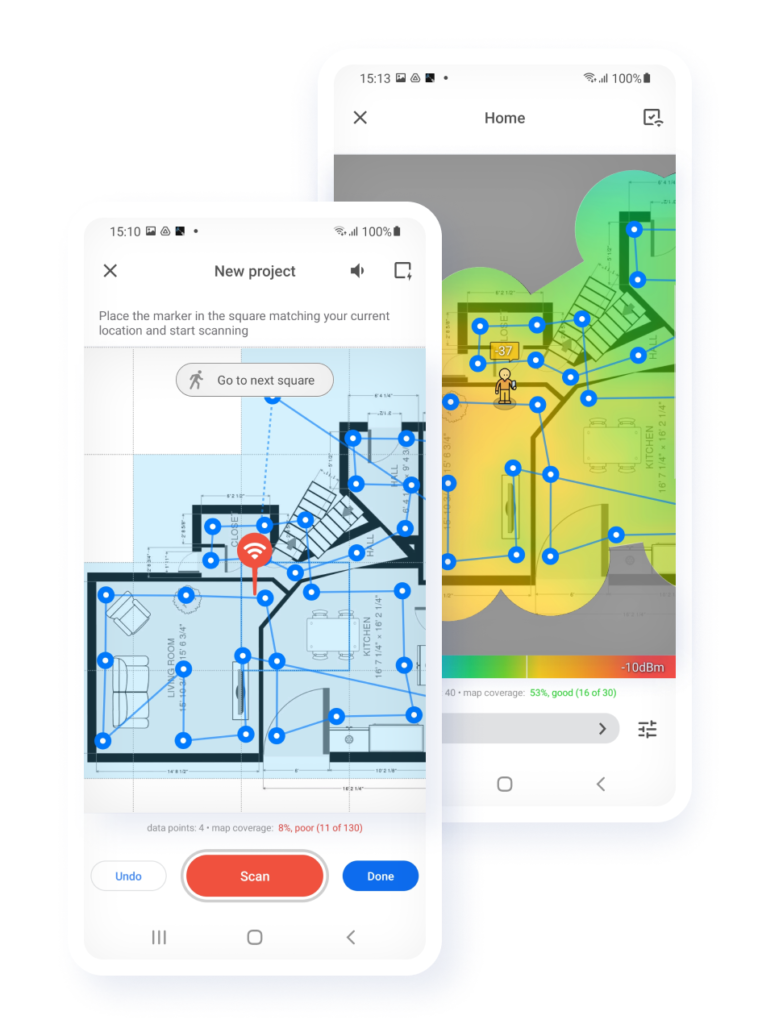
To use Survey Mode in NetSpot, do the following:
Select Survey Mode in the top toolbar.
Create a new survey project and enter its name and description.
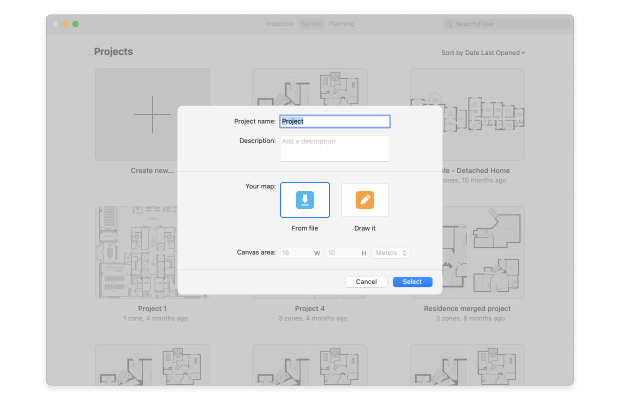
Either create or upload a map of the area you want to survey and calibrate it.
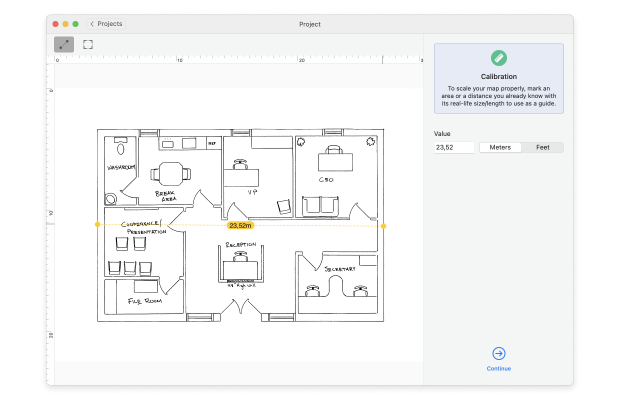
Take measurements to gather the necessary data about your WiFi.
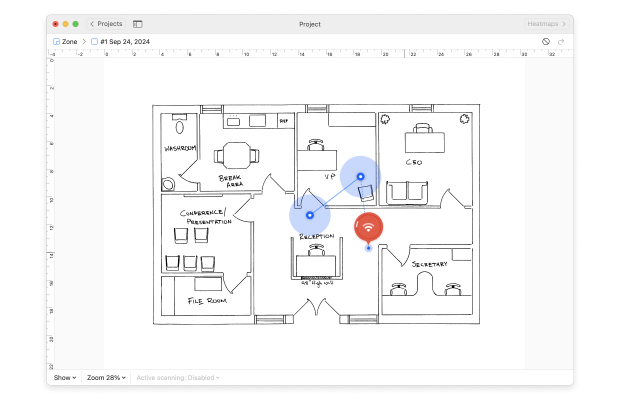
Convert your measurement results into heatmaps to see how coverage and performance are changing in your room.
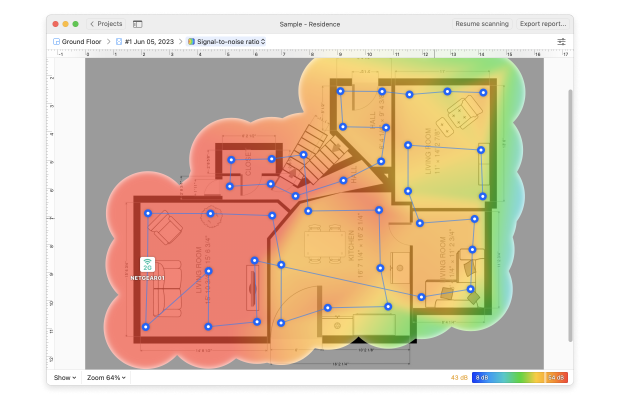
With NetSpot heatmaps, you can quickly identify weak spots, compare coverage in different rooms, and decide whether simply moving your router is enough or if it's time to upgrade. For more information about Survey Mode, please visit visit the official support page.
Perform an in-depth visual analysis and troubleshoot your WiFi network with comprehensive color-coded heatmaps.
3. Fix Your WiFi Network
After diagnosing your network with NetSpot, the next step involves implementing solutions based on the insights gained to stop your internet connection from dropping and reconnecting.
As we've already mentioned in this article, the solution could be as simple as changing your router's location, adjusting its settings, or upgrading your equipment. To learn more about optimizing your WiFi network, we recommend checking out our top 15 ways to boost WiFi and our how to increase WiFi speed articles.
Conclusion
Most WiFi drops have a practical explanation — and a practical solution. Typically, it's a combination of factors: coverage gaps, interference, router limitations, device settings, or issues with the internet service provider.
Test everything in a sensible order, changing one parameter at a time, and confirming what actually improves the situation. If you want a clearer picture of what's happening on the air, WiFi troubleshooting tool like NetSpot can help you check your signal and channel status and make actionable adjustments.
Why Does My WiFi Keep Disconnecting — FAQs
There are many potential reasons, including weak signal, interference, router issues, Wi-Fi adapter problems, or malware. That is why it is a good idea to use Wi-Fi analyzer app like NetSpot to diagnose the specific issue affecting your connection.
The easiest way to determine if your router is the culprit is to try a different router. You can borrow one from a friend, family member, or neighbor, or even use a spare one if you have it.
An unstable internet connection can be caused by issues with your ISP, router, WiFi settings, and other less common factors. Scanning your network with a tool like NetSpot can help pinpoint the exact issue.
We recommend you start by restarting your router. If that doesn't help, then you should use a WiFi analyzer app like NetSpot to determine if the signal transmitted by your router is sufficiently strong and not affected by other nearby WiFi networks.
