Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
Wi-Fi Channels Explained: Optimize Your Wireless Network
Discover what Wi-Fi channels are, why choosing the right channel improves network speed and stability, and how to easily identify interference.
Wi-Fi surrounds us on every floor and street corner, yet most users have no idea which radio “lanes” their routers occupy — or that those lanes even exist. This article pulls the curtain back on Wi-Fi channels across the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands, explains how crowded channels throttle speed, and shows how the WiFi Channel Scanner lets you spot interference and lock in the fastest, cleanest channel with just a few clicks.
- Wi‑Fi Channels: What They Are and Why They Matter
- Overview of 2.4 GHz WiFi Channels
- Wi-Fi channels 1, 6, and 11
- Non-Overlapping Channels
- Which Wireless Channel to Use in a Crowded Space
- 5 GHz channel band
- 6 GHz Channel Band
- Three main reasons for WiFi interference
- Common Mistakes When Selecting Wi-Fi Channels
- How to Find the Best Wi-Fi Channel
- How to Change Your Router’s Wi-Fi Channel
- Select the right Wi-Fi channel with NetSpot — the top WiFi channel analyzer
- WiFi Channels — FAQs
Wi‑Fi Channels: What They Are and Why They Matter
If you’ve ever wondered how your devices communicate wirelessly, it comes down to something called Wi-Fi channels. Wi-Fi routers and devices transmit data using specific frequency bands — commonly the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and, with the latest advancements, the 6 GHz bands.
Each of these frequency bands is divided into smaller segments known as Wi-Fi channels. Think of these channels as dedicated lanes on a wireless highway, each one providing a clear path for data traffic. This system helps multiple routers and devices in a shared area avoid congestion by using separate channels, minimizing interference, and ensuring smoother data flow.
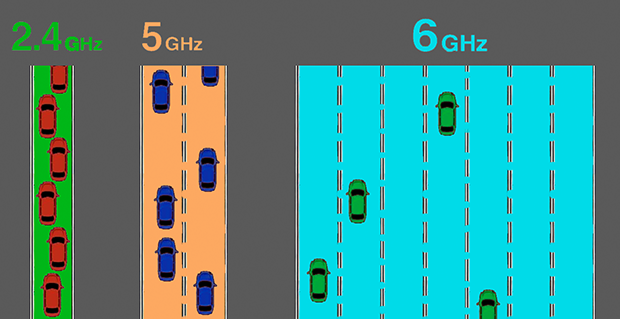
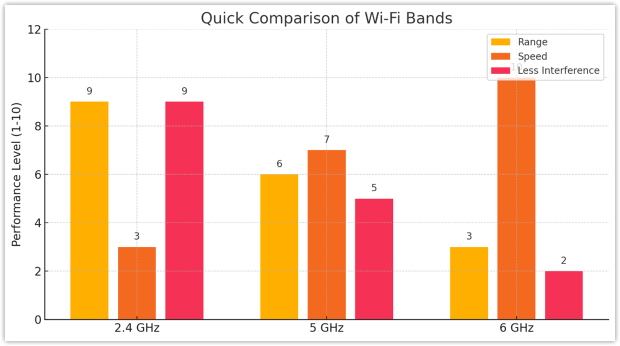
To clearly visualize the differences between these bands:
- 2.4 GHz band: This band offers the widest coverage range, reaching further distances and penetrating walls effectively, but at the cost of lower data speeds. It’s ideal for connecting devices placed further from the router, such as smart home gadgets and IoT devices.
- 5 GHz band: With shorter range compared to the 2.4 GHz band, the 5 GHz band compensates by providing significantly faster data speeds. This makes it perfect for high-bandwidth tasks like video streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing, particularly when devices are relatively close to the router.
- 6 GHz band: The 6 GHz band delivers ultra-fast speeds and minimal interference, offering the highest data throughput available for Wi-Fi today. However, it has the shortest effective range and is best suited for high-performance, cutting-edge devices in close proximity, especially in less obstructed environments.
Because each band offers a different number of channels, its overall capacity changes dramatically. The 2.4 GHz band provides only three non‑overlapping channels, so traffic builds up quickly and speeds drop. In contrast, both 5 GHz and 6 GHz expose dozens of clean, separate channels, giving your devices much more elbow‑room to stay fast and stable.
Understanding and managing Wi-Fi channels helps you optimize your network’s performance, reduce interference from neighboring networks, and achieve faster and more reliable connections.
Let’s see how these differences translate visually in the chart below.
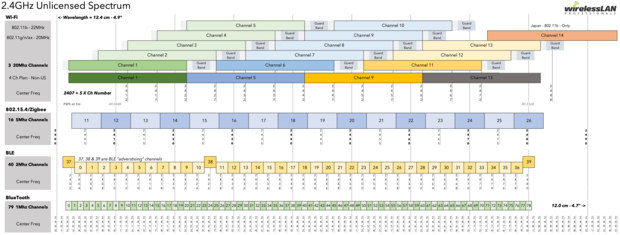
Overview of 2.4 GHz WiFi Channels
The 2.4 GHz band has 14 channels, but some countries don’t allow them all. In Europe, only channels 1 to 13 are available. In North America, channels 12, 13 are allowed only under low power conditions, and channel 14 isn’t allowed at all.
The channels are spaced 5 MHz apart from each other. The only exception is channel 14 [2], which has a 12 MHz space before it.
| Channel | Frequency range |
| 1 | 2401–2423 MHz |
| 2 | 2406–2428 MHz |
| 3 | 2411–2433 MHz |
| 4 | 2416–2438 MHz |
| 5 | 2421–2443 MHz |
| 6 | 2426–2448 MHz |
| 7 | 2431–2453 MHz |
| 8 | 2436–2458 MHz |
| 9 | 2441–2463 MHz |
| 10 | 2446–2468 MHz |
| 11 | 2451–2473 MHz |
| 12 | 2456–2478 MHz |
| 13 | 2461–2483 MHz |
| 14 | 2473–2495 MHz |
Wi-Fi channels 1, 6, and 11
In your router's settings there are channel settings. Most routers have channel settings set to "Auto", but if you look through the list, there are at least a dozen of WLAN channels. So how do you know which WiFi channels are faster than the others in that list? Choosing the proper WiFi channel can vastly improve your WiFi coverage and performance. But even if you find the fastest channel there it doesn't always mean you should select it right away.
Various frequency bands (2.4GHz, 3.6 GHz, 4.9 GHz, 5 GHz, and 5.9 GHz) have their own range of channels. Usually routers will use the 2.4GHz band with a total of 14 channels, however in reality it may be 13 or even less that are used around the world.
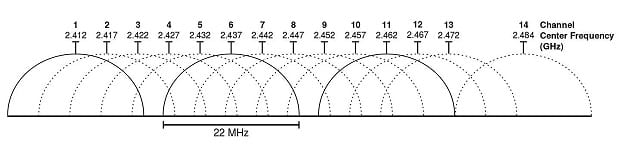
All Wi-Fi versions through 802.11n (a, b, g, n) work between the channel frequencies of 2400 and 2500 MHz. These 100 MHz in between are split in 14 channels 20 MHz each. As a result, each 2.4GHz channel overlaps with two to four other channels (see diagram above). Overlapping makes wireless network throughput quite poor.
Most popular channels for 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi are 1, 6, and 11, because they don’t overlap with one another. You should always try using channels 1, 6, or 11 when on a non-MIMO setup (i.e. 802.11 a, b, or g). The table below lists all 11 Wi-Fi channels that are available in North America and specifies the exact frequency range of each:
| Channel number | Bottom of channel | Center frequency | Top of channel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2401 | 2412 | 2423 | |
| 2 | 2406 | 2417 | 2428 | |
| 3 | 2411 | 2422 | 2433 | |
| 4 | 2416 | 2427 | 2438 | |
| 5 | 2421 | 2432 | 2443 | |
| 6 | 2426 | 2437 | 2448 | |
| 7 | 2431 | 2442 | 2453 | |
| 8 | 2436 | 2447 | 2458 | |
| 9 | 2441 | 2452 | 2463 | |
| 10 | 2446 | 2457 | 2468 | |
| 11 | 2451 | 2462 | 2473 |
Non-Overlapping Channels
As said above every wireless channel on the 2.4 GHz spectrum is 20 MHz wide. When using 802.11n with 20 MHz channels, choose the 1, 6, and 11 ones. If going to use 40MHz channels, take into consideration that the airwaves may be congested, unless you live in a house in the middle of a very large property.
The whole spectrum is 100 MHz wide and the channel centers are separated by 5 MHz only. This leaves no choice to eleven channels but to overlap.
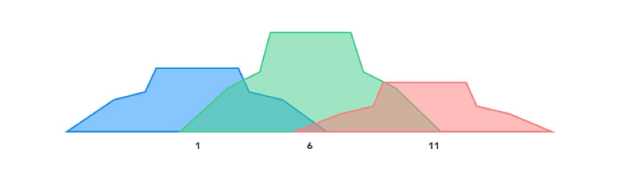
Which Wireless Channel to Use in a Crowded Space
Channels 1, 6, and 11 are your best choice for the highest throughput and minimal interference because they don’t overlap with one another—that’s why they’re called non-overlapping.
However, they still overlap with their neighboring channels. For example, Channel 1 overlaps with channels 2, 3, 4, and 5. You can use a WiFi analyzer to scan WiFi channels and determine which of the three non-overlapping channels are the least likely to suffer from signal interference.
A WiFi channel scanner can also tell you which of the three non-overlapping channels is used by the smallest number of WiFi routers. The best WiFi channel scanners can even determine how strong the interference emitted by individual WiFi routers is.

Inspect, compare, survey, and analyze WiFi networks with NetSpot. Optimize your WiFi network for maximum performance.
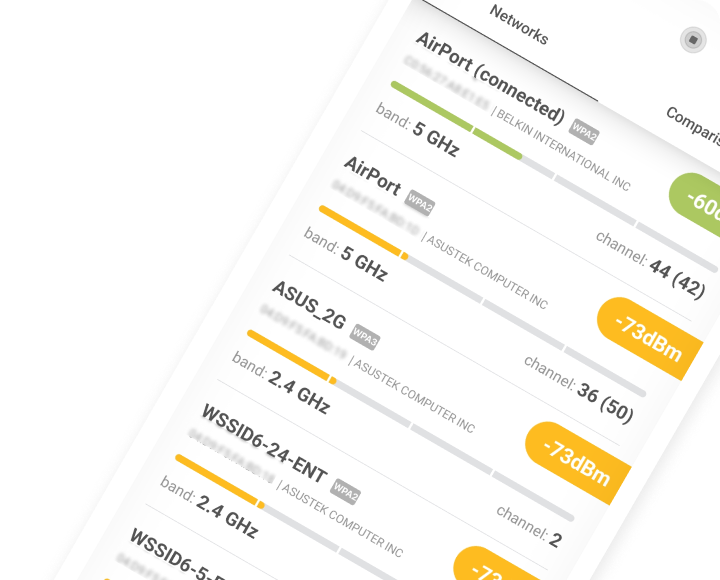
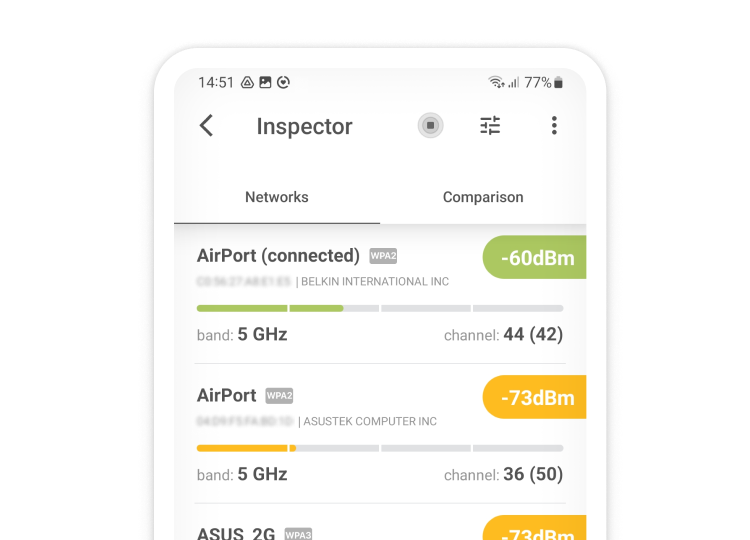
What to Do When WiFi Channels 1, 6, and 11 Are Crowded?
In situations where all of the three non-overlapping WiFi channels are crowded, you should switch to the 5 GHz band. Not only is this band used much less frequently than the 2.4 GHz band, but there are also far more 5 GHz channels to choose from.
You don’t even need to manually select the best 5 GHz channel because most WiFi routers can do it automatically for you, which can’t be said about the selection of the best 2.4 GHz channel.
5 GHz channel band
The 5 GHz (802.11n and 802.11ac) band actually offers way more free space at the higher frequencies. It offers 23 non-overlapping 20MHz channels.
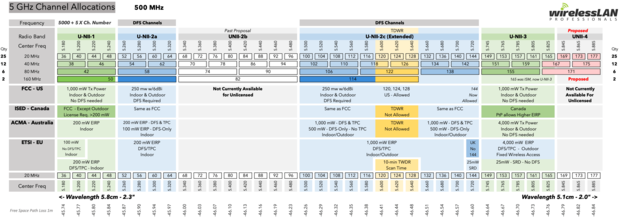
Starting with 802.11n and going to 802.11ac, wireless technology became much more advanced. If you bought a WiFi router within the last couple of years, then you probably have a decent 802.11n or 802.11ac router. Most of them have a hardware inside that automatically selects the proper WiFi channel and adjusts the output power thus boosting throughput and cutting down the interference.
5 GHz channel band compatibility:
- 802.11n: Released in 2009, this emendation to the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless-networking standard is the first mainstream version of the IEEE 802 set of LAN protocols that can be used in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands.
- 802.11ac: Released in 2013, 802.11ac extended channel binding from 40 MHz in 802.11n to optional 160 MHz and mandatory 80 MHz channel bandwidth for stations, resulting in multi-station throughput of at least 1 gigabit per second and single-link throughput of at least 500 megabits per second (500 Mbit/s).
- 802.11ax: Also called Wi-Fi 6 by Wi-Fi Alliance, 802.11ax is the latest version of the IEEE 802.11 standard, designed to operate in all band spectrums between 1 and 7 GHz. 802.11ax Wi-Fi routers were demonstrated to achieve a top speed of 11 Gbit/s, in part thanks to their ability to avoid interference with neighboring networks.
Using the 5GHz band and having decently thick walls as well as the general lacking of 5GHz devices usually means that there is a very little interference in your space. In cases like this you may benefit from using the 40, 80, and 160MHz channels.
Ideally, as everyone gradually upgrades their hardware and starts using 5GHz band, having to select the proper WiFi channel will become obsolete. It is especially applicable to MIMO setups (up to eight in 802.11ac), when it is a better idea to let your router do its own thing. Of course there will be custom cases like fine-tuning the channel selection for your router.
Eventually, even the 5GHz will fill up, but by the time it happens we should be able to figure higher WiFi channel frequencies out. Or maybe entirely new antenna designs will be created for the high-end demands of wireless networking world.
6 GHz Channel Band
In addition to the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, WiFi users can now take advantage of the 6 GHz channel band, which was made available for unlicensed use by the FCC in 2020, creating lots of excitement across the entire WiFi ecosystem.
What Is 6 GHz WiFi Band?
The 6 GHz WiFi band represents the portion of the radio spectrum that extends from 5.925 GHz to 7.125 GHz. As such, the 6 GHz WiFi spectrum provides additional 1,200 MHz of uncongested bandwidth as the image below illustrates.
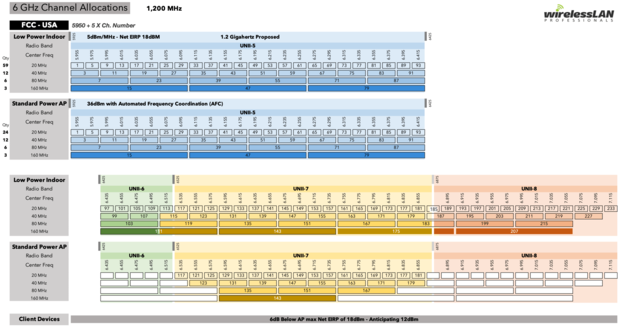
The 6 GHz WiFi band is split into 109 channels to support many simultaneously connected devices, and it supports channel bonding for the creation of the following wide and superwide channels:
- seven 160 MHz-wide channels
- fourteen 80 MHz-wide channels
- twenty-nine 40 MHz-wide channels
- fifty-nine 20 MHz-wide channels
These wide and superwide channels can support Gigabit speeds and ensure extremely low latency, making them perfect for 4K and 8K streaming and other demanding applications.
6 GHz Channel Band Compatibility
Rather confusingly, the 6 GHz channel isn’t supported by WiFi 6 (802.11ax-2019). Instead, support for the standard was introduced only with the release of the WiFi 6E (802.11ax-2020) standard.
Besides 6 GHz WiFi channels, WiFi 6E also supports channels in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, making it the most versatile WiFi generation to date.
6 GHz vs 5 GHz WiFi
The 5 GHz WiFi frequency band has been available much longer than the 6 GHz frequency band. It was first introduced with the release of the 802.11a in 1999. Since then, it was included in 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax.
The 5 GHz band offers 23 non-overlapping 20 MHz channels, so less than half compared with the 6 GHz band. Its maximum data transmission rate also isn’t as impressive as the maximum transmission rate of the 6 GHz band (around 7 Gbps vs 9.6 Gbps).
Three main reasons for WiFi interference
All Wi-Fi connections can be negatively affected by electromagnetic interference, also called radio-frequency interference, which happens for three main reasons:
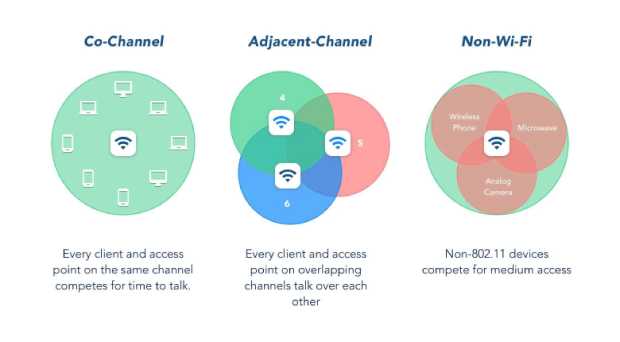
Reason 1: Co-Channel Interference
In networks where devices take turns to talk, it takes time for each of them to wait for their turn. Therefore, the more devices the longer the wait time. This type of Wi-Fi interference isn’t actually electromagnetic interference. Instead, it’s a result of Wi-Fi routers doing their best to give one another room to transmit data.
Think back to when you were in elementary school and your teacher asked the whole class a question. The chances are that multiple kids started shouting at once and nobody could hear anything properly. That’s basically what co-channel interference is, which is why Wi-Fi routers take turns and politely wait for one another to finish.
Reason 2: Adjacent-Channel Interference
Adjacent-channel interference happens when clients on overlapping channels talk at the same time. Wi-Fi channel selection is crucial in cases like this. Such channel-related interferences can be cut down or excluded by choosing the proper Wi-Fi channel for your network.
NetSpot can help you reveal which Wi-Fi channels are cluttered the most so you can avoid them and use other channels instead, preferably channels 1, 6, or 11 because these three channels are non-overlapping. Fortunately, modern Wi-Fi routers are able to cope with adjacent-channel interference much better than older routers, many of which default to the same Wi-Fi channel.
Reason 3: Non-Wi-Fi interference
In addition to Wi-Fi routers, there are many other electronic devices that can interfere with the 2.4 GHz band. Some interfere with it because they use it to wirelessly transmit data, such as security cameras, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, and smartphones, while others interfere with it because they emit a large amount of electromagnetic radiation, such as microwaves and other appliances.
To avoid non-Wi-Fi interference, it’s important to place your Wi-Fi router far away from all sources of electromagnetic radiation, preferably also away from solid objects, including walls, large pieces of furniture, and so on.
A WiFi channel scanner like NetSpot helps you see through the network and choose the proper channel or reduce WiFi interference. Using NetSpot channel scanner will help you improve your 2.4 GHz WiFi network performance.
Common Mistakes When Selecting Wi-Fi Channels
Choosing a channel isn’t just about grabbing the one with the strongest raw signal. A common pitfall is focusing purely on RSSI while ignoring how many neighboring networks already camp on that same frequency. When several routers share a channel, Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) forces them to “take turns,” and throughput drops even if the signal looks great on paper.
Another frequent mistake is picking an only-partially-overlapping channel instead of one that fully overlaps with nearby traffic. Paradoxically, full overlap (for example, two networks both on channel 6) often performs better than partial overlap (channels 4 and 6) because fully overlapping radios can negotiate airtime more efficiently, whereas partially overlapping ones just treat each other as noise.
Users also tend to leave routers in auto-channel mode and forget to rescan. Interference patterns shift over time as neighbors install new gear or power up additional devices. Regular checks with a tool like NetSpot reveal when your “good” channel has turned into a bottleneck and help you pivot before the slowdown becomes noticeable.
Finally, widening the channel to 40 MHz or more without verifying spectrum congestion can backfire. A wider lane only helps if it’s clear; otherwise, you are simply occupying extra space and creating even more interference for yourself and everyone else. Visualizing live channel distribution in NetSpot lets you decide whether sticking to a narrower 20 MHz lane will actually yield faster, cleaner throughput.
How to Find the Best Wi-Fi Channel
After learning so much useful information about WiFi channels, you’re probably anxious to find the best WiFi channel in your area and configure your router to use it so that you can enjoy a faster and more stable connection to the internet.
In this section, we provide step-by-step instructions on how you can do just that on every major platform. Here’s how to find the best WiFi channel on Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS.
Windows
Windows provides a native way of finding the best WiFi channel, but it relies on a rather unintuitive command-line application, called netsh. This application is included with all versions of Windows starting from Windows 2000, and its main purpose is to allow local or remote configuration of network devices such as the interface.
Here’s how to use netsh as a wireless channel scanner for Windows:
- Press Win + R on your keyboard.
- Type “cmd” and press Enter.
- Enter “netsh wlan show all” in the Command Prompt and press Enter.
- Scroll down until you see a section called “SHOW NETWORKS MODE=BSSID”.
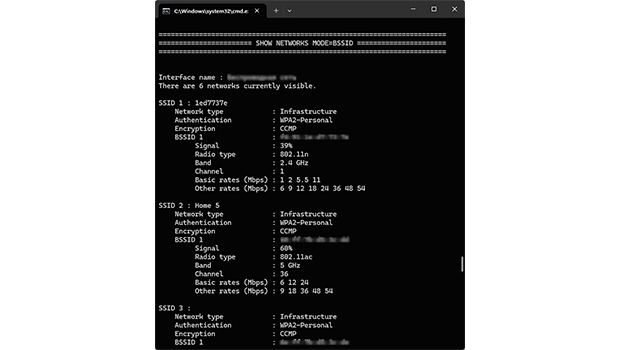
- Analyze which channels are used the most by networks in your area.
Needles to say, using netsh as a WiFi channel scanner for Windows is slow and cumbersome. Fortunately, more convenient WiFi channel scanner Windows apps do exist, and NetSpot is the one we recommend to all home users and professionals alike because of its intuitive user interface and impressive capabilities.
To find the best WiFi channel with NetSpot on Windows:
Download and install the Windows version of NetSpot.
Launch NetSpot. Before starting, make sure Inspector mode is selected. It shows in-depth network metrics and live signal-strength graphs, so you can spot interference the moment it appears.
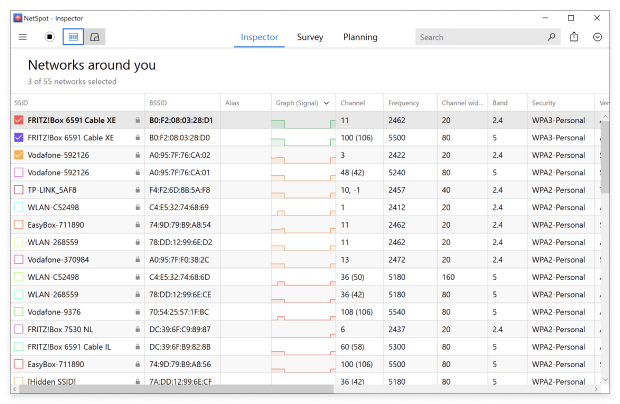
Sort the detected Wi-Fi networks by channel to see, at a glance, which frequencies are clear and which are congested. The automatic ordering spares you the chore of scrolling through a long list of SSIDs. If you’re after other details — like signal strength or band — just switch the sort criterion and get a complete snapshot of your Wi-Fi landscape.
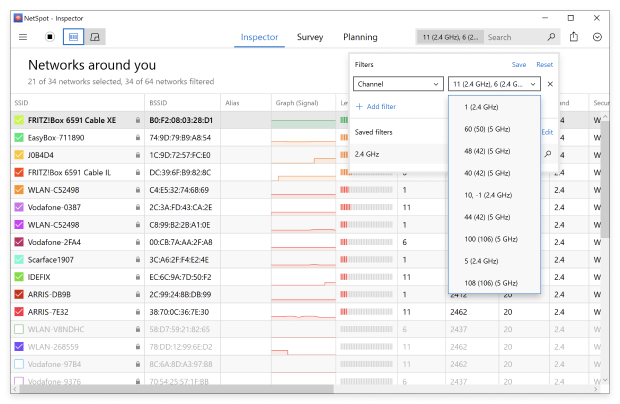
Check which of the non-overlapping channels (1, 6, or 11) is least occupied. But don’t overlook nearby signal strengths — sometimes a neighboring network with a strong signal can create interference even if the channel appears clear
Configure your router to use the least used channel. To change the channel, you’ll need to access your router’s web interface. As explained in more detail below, this typically involves entering the router’s IP address into a web browser, logging in, and navigating to the wireless settings.
As you can see, NetSpot is much simpler to use than netsh, and it offers considerably more features that make troubleshooting WiFi issues a breeze.
NetSpot can also display a channel overlap graph that clearly shows which networks are overlapping:
Launch NetSpot and select Inspector mode.
Select all WiFi networks you want to analyze.
Locate the “Signal Level & Noise Graphs” button just beneath the upper toolbar on the left side and click it.
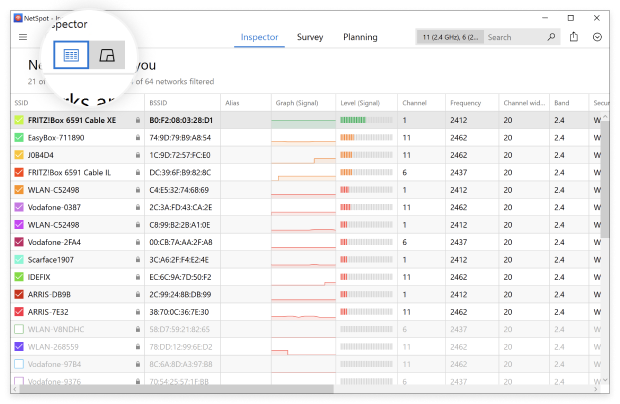
Navigate to the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, or 6 GHz Channels tab to visualize which networks overlap in each band.
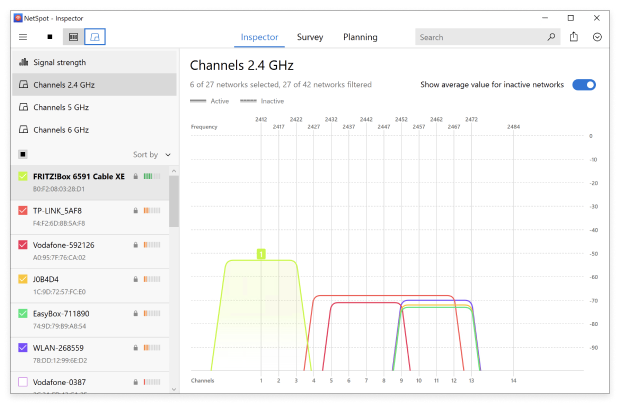
The channel-overlap graph shows at a glance which access points fight for the same slice of spectrum, so you spot interference in seconds.This allows you to identify whether channels are experiencing full or partial overlap. Full overlap is often preferable to partial because networks can ‘negotiate’ and minimize interference.
macOS
macOS comes with a built-in WiFi channel scanner, and you can access it by clicking the WiFi network icon in the menu bar and selecting the Open Wireless Diagnostics option. Don’t pay attention to the prompts and, instead, click Window > Scan in the Title Bar.
You should see a list of all WiFi networks available in your local area. To obtain the most accurate results, click the Scan Now button in the bottom-right corner to refresh the list. The left pane displays a convenient summary of the scan results, including the best WiFi channels.
Alternatively, you can use a third-party WiFi analyzer app like NetSpot and make your life a bit easier while obtaining more comprehensive results. NetSpot not only simplifies the process but also offers powerful tools like real-time analysis and detailed visualizations that help identify network issues quickly.
With NetSpot, finding the most suitable WiFi channel is a matter of a few simple clicks, and you don’t even need to spend any money because you can use NetSpot’s powerful Inspector mode for free.
Follow the steps below to use NetSpot as your Mac WiFi channel scanner:
Download and install the NetSpot app on your Mac.
Launch NetSpot and click Inspector on the top-center panel.
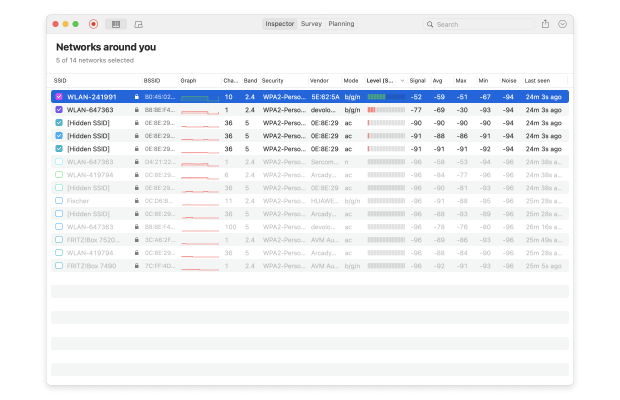
Sort the discovered WiFi networks by their channel. Sorting the discovered Wi-Fi networks by channels or signal level provides a clear view of channel congestion and potential conflicts. This feature helps to choose channels with minimal interference more effectively.
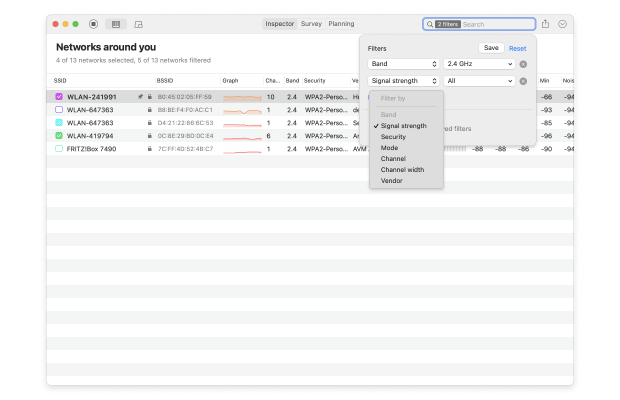
Determine which non-overlapping channel (1, 6, and 11) is utilized the least.
Configure your router to use the least used non-overlapping channel.
NetSpot wireless channel scanner Mac app can also visualize WiFi channel distribution, allowing you to see at a glance which channels are used the most by selected WiFi networks.
To visualize WiFi channel distribution with NetSpot, select each WiFi network you want to plot on a graph and click “Signal level and noice graphs” button in the top-left corner of the main window.
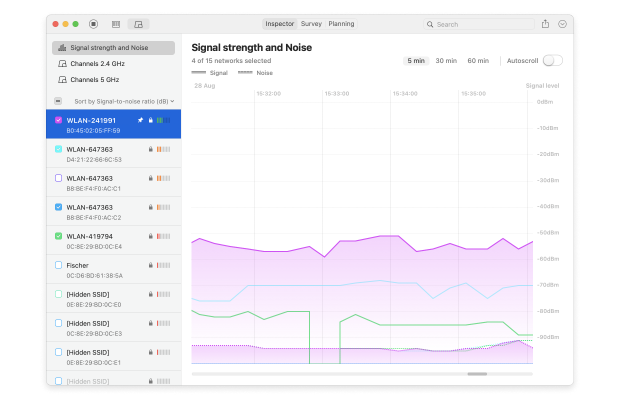
Finally, switch to the Channels 2,4 GHz tab.
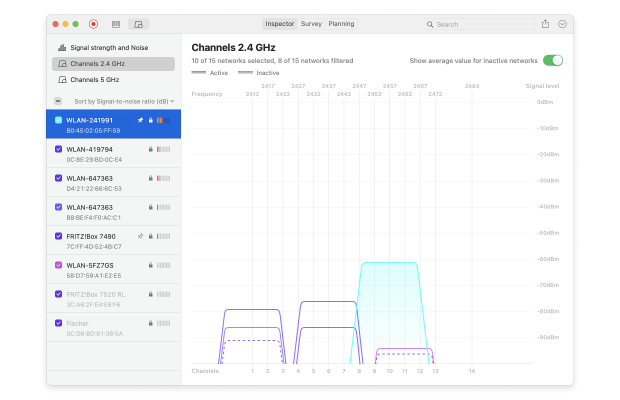
These and other features make NetSpot the best Mac WiFi channel scanner available.
Linux
If you’re using a popular Linux distribution like Ubuntu, you don’t need to install a third-party WiFi channel scanner to find the best WiFi channel in your area. You can just use a command-line utility called iwlist, whose purpose is to display useful information from a wireless network interface, such as the WiFi card in your laptop or the USB WiFi dongle connected to your desktop computer.
Follow these steps to find the best WiFi channel using iwlist:
Open Terminal.
Check what interface you are using the “ip link” command.
Enter the following command to see a summary of what is being used:
- sudo iwlist wlan0 scan | grep Frequency | sort | uniq -c | sort -n>
Make sure to replace wlan0 with the interface specified after running the “ip link” command (such as wlp3s0).
Android
Unfortunately, the Android operating system doesn’t let you see which channel a WiFi network uses, so it’s impossible to determine which WiFi channels are suitable and which are not without a third-party WiFi channel scanner app.
There are several WiFi channel scanner apps for Android that helps find the best WiFi channel using a smartphone or tablet, but we recommend the Android version of NetSpot because you can download it for free directly from Google Play Store to see important WiFi parameters, including WiFi channels, in real-time. NetSpot for Android is just as easy to use as its desktop counterpart, and it supports 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz channel bands.
To find the best WiFi channel using NetSpot for Android:
Download NetSpot for Android from Google Play Store.
Launch the app.
Select the Inspector mode.
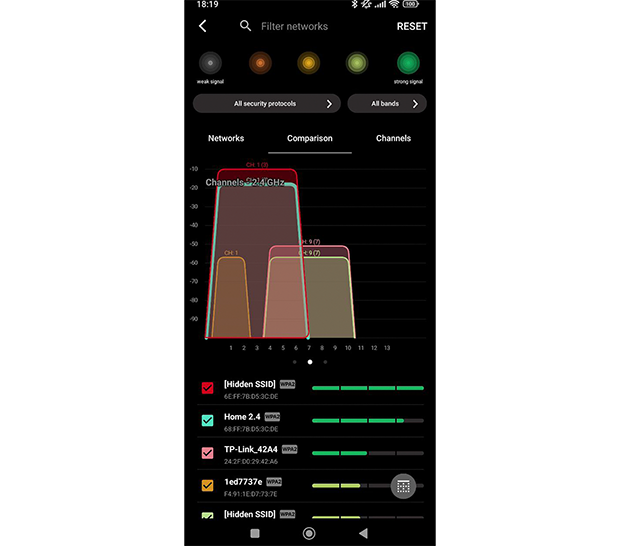
Switch to the Comparison tab and instantly see which channels in the 2.4 GHz, 5GHz, and 6 GHz bands are used the most. By swiping the graph from right to left, you can switch from the 2.4 GHz to the 5 GHz band. If your device supports 6 GHz, you can also access the 6 GHz tab.
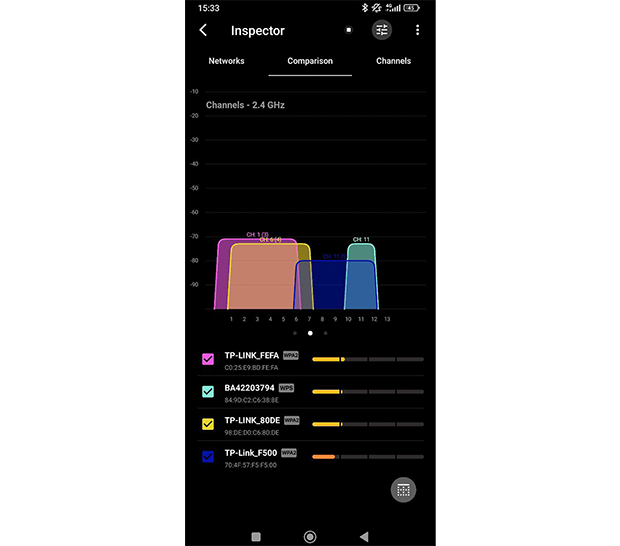
You can further customize the analysis by excluding specific channels from the comparison by tapping the small checkbox next to them. This allows you to focus on the channels you are considering and ignore irrelevant ones.
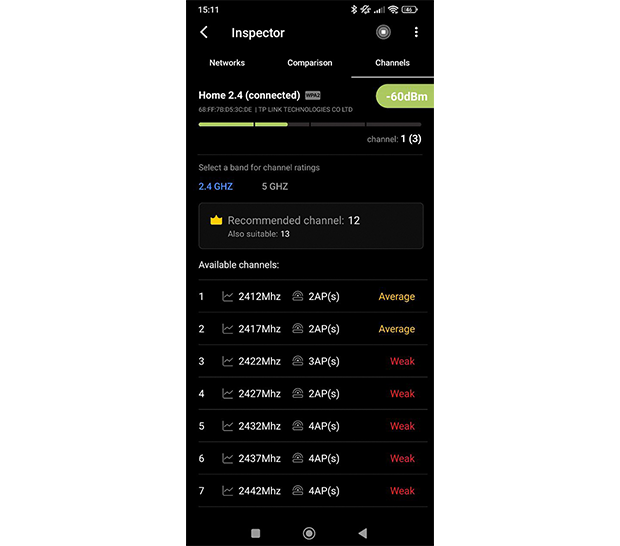
If you’re unsure which channel to choose, the app will guide you. Switch to the Channels tab in NetSpot for Android to analyze channel usage and find the best available option for optimizing your Wi-Fi network. The tab highlights the recommended channel, typically the least congested and most suitable for your network, while also providing detailed information such as performance rating (Poor, Weak, Average, Good).
NetSpot’s simplicity is just one of many things that make it the best WiFi channel scanner for Android. You can exclude a certain channel from the comparison by tapping the small checkbox next to it.
NetSpot supports modern standards such as Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E, making it ideal for analyzing networks on the 6 GHz band. Its compatibility with Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS ensures users can seamlessly access its features on their preferred devices. This flexibility is especially valuable for optimizing performance with the latest router technologies.
With an intuitive interface, real-time monitoring, and advanced tools like channel overlap visualization, NetSpot remains a versatile solution for both casual users and professionals. Its ability to adapt to multiple platforms makes it a go-to choice for simplifying Wi-Fi optimization.
iOS
Not many iPhone and iPad users know that AirPort Utility, whose purpose is to manage WiFi network and AirPort base stations, contains a fairly capable WiFi scanner that you can use to discover the best WiFi channel available in your area.
This is how to activate and use it:
Download AirPort Utility from the App Store.
Open Settings and go to the AirPort Utility Settings screen.
Turn on the Wi-Fi Scanner feature at the bottom.
Launch AirPort Utility and tab the blue Wi-Fi Scan button in the top-right corner.
Set the desired scan duration and tap Scan.
How to Change Your Router’s Wi-Fi Channel
To change WiFi channel, you first need to enter its admin interface. This is usually done by entering a specific IP address in your web browser (it should be printed on the bottom of your router), but some newer routers come with a companion smartphone app.
The IP address should take you to the login page to your router’s admin interface. Unless you’ve changed the default login name and password to something else, you should be able to log in by entering “admin” as both the username and password. If it doesn’t work, consult the manual that came with your router or get in touch with the manufacturer directly.
Once you’re inside the admin interface, you need to find the WiFi channel setting so that you can change it to your preferred channel. Because all routers are different, we can’t give you detailed instructions here, but it should be located under Wireless Settings or Advanced Settings.
After you’ve changed the WiFi channel, the only thing left to do is to restart your router. As you can see, learning how to change a WiFi channel on your router is easy, and the whole process takes just a few minutes.
Select the right Wi-Fi channel with NetSpot — the top WiFi channel analyzer
As explained in this article, channel overlapping leads to co-channel interference, which can dramatically degrade WiFi performance and cause annoying slowdowns and other issues. Without a WiFi analyzer like NetSpot, it can be very difficult and tedious to solve issues created by channel overlapping and determine which WiFi channel would be more suitable.
The good news is that co-channel interference can be easily eliminated by proper WiFi channel planning. NetSpot is very good at visualizing the networks to help you make the right decision. With NetSpot's visualization you will immediately see the cause of the wireless issues and how to eliminate them.
You can get the recommendation on which channel to use and the best thing about it — you don't have to be a WiFi professional to choose the optimal channel for your network. All you need to do is just open NetSpot app and click Discover. Click the "Channels 2.4 GHz" header to see where Wi-Fi channels are overlapping. Look for the channel (out of 1, 6 and 11) with the least number of networks present on it.
The “Show average value for inactive networks” option is enabled by default in NetSpot, which means you'll see even currently inactive networks and their average values. You can disable this option when you don't need the data for currently inactive networks. The active networks are shown in solid lines on the graph.
In the above graph the selected network is operating on channel 5, and overlaps with channels 2 and 8. You can see that channels 6 to 9 have the smallest number of networks and overlapping is not that bad at all. So in this particular case if you need the best WiFi channel, choose from channels 6 to 9.
WiFi Channels — FAQs
The best WiFi channel scanner and analyzer is easy to use, it supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz channel bands, and delivers accurate data in real-time. When choosing a WiFi analyzer, you need to make sure that it supports your operating system and offers all the features you need to solve all kinds of WiFi-related issues. We could recommend you NetSpot for macOS, Windows, and Android.
Channels 1, 6, and 11 are the best channels for WiFi in the 2.4 GHz band because they are the only non-overlapping channels available. Follow our best practices for WiFi channel planning .
The purpose of a WiFi channel analyzer is to gather as much information about surrounding WiFi networks as possible to help you troubleshoot WiFi-related problems and improve the performance of your network.
You can easily analyze WiFi channels using a free WiFi channel analyzer app, like NetSpot, for Windows, macOS, Linux, or Android.
UNII-1 channels (36, 40, 44, 48) are often considered to be the best 5 GHz channels for home use, but most 5 GHz routers are capable of automatically selecting the best channel.
All WiFi channels are more than capable of providing the maximum data transfer rate your router is capable of achieving, but only if they are not too crowded. That’s why it’s important to use a WiFi analyzer to determine which WiFi channel is utilized the least and thus likely the fastest.
Both 20 and 40 MHz channels have their pros and cons. Because 20 MHz channels are narrower, they don’t suffer from as much interference as wide 40 MHz channels. On the other hand, 40 MHz channels allow for greater speed and faster transfer rates.
Finding the most suitable WiFi channel can improve your wireless experience tremendously. But it's not just the speed you should be looking at, the overlapping is an important factor as well. The most popular WiFi channels for 2.4 GHz frequency are 1, 6, and 11, because they don’t overlap with each other. Use these channels with a non-MIMO setup (i.e. 802.11 a, b, or g).
The three main reasons for wireless interference are:
- In some networks devices wait for their turn to talk, and when there are a lot of devices, the waiting times grow really long. As a result the co-channel interference is created by Wi-Fi routers giving one another way to transmit data.
- When clients in overlapping channels start talking at the same time, an adjacent-channel interference takes place. Choosing a proper Wi-Fi channel can help you mend this issue. Using such software as NetSpot helps identify the most cluttered channels and choose more suitable ones. Upgrading your routers is a solution as well.
- Interference caused by the devices not related to Wi-Fi is called non-WiFi interference. Security cameras, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, smartphones, and microwave ovens can emit a large amount of electromagnetic radiation and cause signal interruptions. Place your Wi-Fi router away from all such sources.
NetSpot can visualize your network coverage to help you see the possible reasons for any wireless issues. NetSpot can also help you choose the best channel for your network. Simply open the NetSpot app and click Discover; then click the "Channels 2.4 GHz" header to see where Wi-Fi channels are overlapping. Look for the channel (out of 1, 6 and 11) with the least number of networks using it.
You can easily scan for WiFi channels using a wireless channel scanner like NetSpot. NetSpot can scan WiFi channels in the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz band, giving you a comprehensive overview of all wireless activity in your area.
There are three non-overlapping channels in the 2.4 GHz frequency band (1, 6, and 11). The best non-overlapping channel is always the one that’s used the least by other wireless networks in your area, and you can determine which channel that is using a WiFi channel analyzer app.
Yes, it does. Using a channel exposed to too much signal interference can dramatically degrade your WiFi experience, causing slowdowns and even connection drops.
There are fewer channels in the 2.4 GHz band than in the 5 GHz band. For this reason, they are more likely to be affected by signal interference.
A channel represents a specific radio frequency range. Because there are multiple channels, WiFi signals can be separated from one another to prevent interference.
