Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
What Is WiFi 6E and Should I Upgrade to It?
WiFi standards are constantly evolving to keep up with our growing connectivity needs. WiFi 6E, introduced in 2020, brought significant improvements to wireless local-area networks by opening up the 6 GHz band for the first time.
Despite no longer being the latest WiFi standard, WiFi 6E remains relevant and worth considering upgrading to if you crave improvements in speed, coverage, and reliability.
What Is Wi-Fi 6E?
WiFi 6E is the marketing term used to refer to the IEEE 802.11ax standard for wireless local-area networks. The WiFi 6E arrived in 2020, just a year after the introduction of WiFi 6, which is also based on the IEEE 802.11ax standard.
Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E
The biggest difference between WiFi 6 vs WiFi 6E is that the latter WiFi generation supports three different frequency bands (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz), whereas the former supports only two (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz).
The support for the 6 GHz band is a huge deal if you live in an area with more WiFi networks than trees. In such areas, wireless interference tends to be a major problem, causing everyone’s speeds to fluctuate unpredictably and making it difficult to achieve even signal coverage.
In the 6 GHz band, there are 59 additional 20 MHz channels and 29 additional 40 MHz channels, and it’s thanks to them that WiFi 6 speeds can greatly exceed WiFi 6 speeds. That’s why WiFi 6E is also known as High Efficiency Wi-Fi.
| WiFi 6 | WiFi 6E | |
|---|---|---|
| Introduced | 2019 | 2020 |
| IEEE Standard | 802.11ax | 802.11ax |
| Maximum Linkrate (Mbit/s) | 600 to 9608 | 600 to 9608 |
| Supported bands | 2.4/5 | 2.4/5/6 |
What Are the Advantage of Wi-Fi 6E?
We’ve already touched upon some of the main advantages of WiFi 6E, and now is the time to take a closer look at them:
- Speed: While both WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E can theoretically achieve the same maximum linkrate, WiFi 6 routers and devices can’t take advantage of the 6 GHz band to avoid interference-related slowdowns. That’s why WiFi 6E almost always wins when it comes to real-world speeds.
- Coverage: Because WiFi 6E routers and WiFi 6E mesh routers can use three different frequency bands, it’s much easier to achieve great signal coverage even in densely populated urban areas.
- Reliability: The reliability of any WiFi network goes hand in hand with its speed and coverage. Because WiFi 6E networks are faster than those relying on previous WiFi standards, you're much less likely to see your speeds dip below an acceptable level. Likewise, WiFi 6E networks can cover a larger area with a strong signal, so your connection won’t drop just because you take a few extra steps with your smartphone or laptop in the wrong direction.
- Security: All WiFi 6E devices support the latest WiFi standard for security, Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3). The new WiFi standard is backward compatible with WPA2, and it addresses the security issues posed by weak passwords and public networks.
These advantages make upgrading to WiFi 6E worth the effort and necessary financial investment. Just don’t think that WiFi 6E can solve issues caused by poor router placement or configuration. Yes, the better performance of WiFi 6E devices can make them less apparent, but it won’t make them go away.
To fix them, we recommend you use a WiFi network analyzer tool like NetSpot.
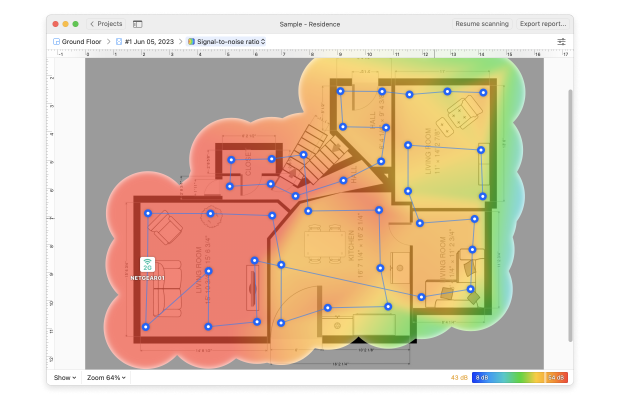
With its help, you can create a detailed coverage map to determine if your router is located in the optimal place, and you can also discover all nearby WiFi networks and see if their configuration doesn’t clash with the configuration your own network.
What Are the Disadvantages of WiFi 6E?
WiFi 6E brings significant improvements over its predecessors, including higher data rates, increased capacity, lower latency, and expanded coverage in the 6 GHz band. However, like any technology, it has its disadvantages. Here are some of the main drawbacks:
- Limited Device Compatibility: As of my last update, not all devices support WiFi 6E. Older devices may not be able to connect to WiFi 6E networks, necessitating dual or tri-band routers that also offer 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks for compatibility. This situation will improve as more new devices are manufactured with WiFi 6E support.
- Cost: WiFi 6E routers and devices tend to be more expensive than their WiFi 5 (802.11ac) and WiFi 6 (802.11ax) counterparts. The premium pricing reflects the new technology and enhanced features, making initial adoption more costly for consumers and businesses.
- Limited 6 GHz Band Availability Worldwide: The availability of the 6 GHz band, crucial for WiFi 6E, varies by country. Regulatory approval is required, and not all countries have opened this spectrum for WiFi use. This limitation affects the global adoption rate and effectiveness of WiFi 6E in delivering its full benefits everywhere.
- Potential for Interference in Dense Environments: While the 6 GHz band is less crowded than 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, there's potential for interference in densely populated areas or in environments with many 6 GHz devices. As adoption increases, managing this congestion will be important to maintain the high performance expected of WiFi 6E.
- Increased Power Consumption: The advanced features of WiFi 6E, such as higher throughput and capacity, may lead to increased power consumption on devices. This can impact battery life, especially in mobile devices and IoT applications, necessitating more frequent charging or larger batteries.
- Indoor Range Limitations: The 6 GHz signals used by WiFi 6E have a shorter range and are less effective at penetrating solid objects like walls and floors compared to 2.4 GHz signals. This could necessitate the use of more access points or mesh systems to ensure comprehensive coverage in larger homes or buildings.
While WiFi 6E presents these disadvantages, its benefits for high-demand environments and future-proofing networks often outweigh the negatives for many users. As the ecosystem matures, costs will likely decrease, and device compatibility will expand, mitigating some of these disadvantages.
WiFi 6E Routers and Mesh Systems
Choosing the best WiFi 6E router or mesh system can be a long and confusing process. To make it easier for you, we’ve put together the following list of our favorite options.
WiFi 6E Routers
The best WiFi 6E routers continue to offer excellent performance for those who want to take advantage of the 6 GHz band without moving to WiFi 7 just yet. Here are our top picks:
- ASUS RT-AXE7800 — This tri-band WiFi 6E gaming router offers a speed capacity of 7800 Mbps, multi-gig internet port, Quad-Core processor, and ample storage. Features include AiProtection Pro security, Instant Guard VPN, advanced parental controls, and support for ASUS AiMesh to expand coverage throughout your home.
- Netgear Nighthawk RAXE500 — A sleek-looking, tri-band Wi-Fi 6E router with a 2.5 Gbps WAN port for multi-gig internet, along with four gigabit LAN ports and two USB ports. Powered by a 1.8GHz quad-core processor, it delivers exceptional 10.8Gbps WiFi speeds and covers up to 3,500 sq. ft. for 60 devices.
- TP-Link Archer AXE75 — In terms of value and performance, the TP-Link Archer AXE75 is one of the best Wi-Fi 6E routers available. It delivers super-fast speeds on the 6 GHz frequency while maintaining low latencies because it's armed with a 1.7 GHz Quad-Core CPU, 512 MB memory, and comprehensive VPN support (OpenVPN/PPTP/L2TP).
WiFi 6E Mesh Systems
Our top WiFi 6E mesh systems continue to provide excellent whole-home coverage with the benefits of the 6 GHz band:
- Netgear Orbi RBKE963 — This quad-band system offers the industry's first quad-band support to deliver lightning-fast speeds up to 10.8 Gbps and coverage up to 9,000 sq. ft. Though expensive at around $1,500 for a pack of three units, it's guaranteed that you won't have to make another WiFi upgrade for a long time.
- TP-Link Deco XE75 — The Deco XE75 has amazing speeds for a mesh system, partly due to the dedicated Deco-to-Deco line. It also features basic parental controls and built-in VPN tools that eliminate the need for third-party products. Its coverage area is 7,200 square feet when you combine three units, and 5,500 square feet if you use just two units.
- eero Pro 6E — The eero Pro 6E is another excellent Wi-Fi 6E mesh system that supports the 6GHz range. It delivers download speeds of 1.44 Gbps at close distance and includes a 2.5 Gbps Ethernet port for multi-gig internet. You can optionally get it with the eero Plus subscription, which gives you everything from parental controls to malware protection to ad blocking.
How Does WiFi 6E Compare to WiFi 7?
| WiFi 6E | WiFi 7 | |
|---|---|---|
| IEEE Standard | 802.11ax | 802.11be |
| Release Date | 2020 | 2024 |
| Maximum Theoretical Speed | 9.6 Gbps | 46 Gbps |
| Frequency Bands | 2.4/5/6 GHz | 2.4/5/6 GHz |
| Maximum Channel Width | 160 MHz | 320 MHz |
| QAM | 1024-QAM | 4096-QAM |
| Multi-Link Operation | No | Yes |
| Key Features | 6 GHz band, OFDMA, Target Wake Time | MLO, Multi-RU, Punctured Transmission |
WiFi 7 (802.11be), officially released in early 2024, is the newest WiFi standard and the direct successor to WiFi 6E. Also known as IEEE 802.11be Extremely High Throughput (EHT), it dramatically improves speed, efficiency, and reliability.
The most notable advancement in WiFi 7 is Multi-Link Operation (MLO), which allows devices to simultaneously connect across multiple bands and channels. This means your device can use 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands at the same time for optimal performance. WiFi 7 also doubles the channel width to 320 MHz (compared to WiFi 6E's 160 MHz), introduces 4K-QAM modulation for 20% higher transmission rates, and implements advanced features like Multi-Resource Unit (MRU) allocation and punctured transmission to maximize efficiency.
The theoretical maximum speed of WiFi 7 reaches an impressive 46 Gbps — nearly five times faster than WiFi 6E's 9.6 Gbps. In real-world scenarios, WiFi 7 can deliver speeds exceeding 5 Gbps to individual devices, so it's great for bandwidth-intensive applications like 8K streaming, VR/AR gaming, and large file transfers.
However, it's important to note that WiFi 7 routers and devices are still relatively expensive, and the full benefits of this new WiFi technology require compatible devices on both ends. For most users at the moment, WiFi 6E remains an excellent choice that offers substantial improvements over older standards at a more accessible price point.
Good to know: NetSpot for Windows already supports WiFi 7, along with WiFi 6E and all older standards.
Conclusion
WiFi 6E extends wireless networking into the 6 GHz band for the first time to deliver faster speeds, reduced interference, and better performance for compatible devices. The WiFi 6E routers and mesh systems recommended in this article offer excellent value and performance, and they're a smart choice even as the newest WiFi standard, WiFi 7, continues to become more readily available thanks to their great price-to-performance ratio.
WiFi 6E — FAQs
WiFi 6E is the marketing term used to refer to the IEEE 802.11ax standard for wireless local-area networks.
WiFi 6E can take advantage of three different frequency bands (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz), whereas WiFi 6 supports only two (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz). Thanks to the additional band, WiFi 6E performs better than WiFi 6.
Even though WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E can theoretically achieve the same maximum linkrate, WiFi 6E can be up to 25 percent faster in the real-world because it supports the 6 GHz band.
No, devices that support only WiFi 6 can’t use WiFi 6E. At the same time, all WiFi 6E routers and mesh systems are backward compatible with WiFi 6, so they can connect WiFi 6-only clients to the internet just fine.
Yes, there are many excellent WiFi 6E mesh systems available. Top options include the Netgear Orbi RBKE963, which offers quad-band support, the TP-Link Deco XE75, which provides excellent value with speeds up to 5,400 Mbps, and the eero Pro 6E, which features a 2.5 Gbps Ethernet port.
If you’re not satisfied with the performance of your WiFi network and have optimized its configuration and coverage using a network analyzer like NetSpot, then a WiFi 6E router might be a great investment.
The Netgear Nighthawk RAXE500 is the fastest WiFi 6E router because it delivers exceptional 10.8 Gbps combined WiFi speeds thanks to its 1.8GHz quad-core processor. Another speed demon is the ASUS RT-AXE7800, which offers impressive speeds at a more affordable price point.
No, WiFi 7 is significantly faster than WiFi 6E. While WiFi 6E has a theoretical maximum speed of 9.6 Gbps, WiFi 7 (802.11be) can reach up to 46 Gbps in theory, so it's nearly five times faster. WiFi 7 also introduces Multi-Link Operation (MLO) that allows devices to use multiple bands simultaneously. As a result, you're less likely to experience sudden performance drops due to signal interference.
WiFi 7 is technically superior to WiFi 6E, offering higher speeds, lower latency, and advanced features like MLO and 320 MHz channels. However, "better" depends on your specific needs. For most users in 2025, WiFi 6E offers better value because it provides excellent performance at a more accessible price point, and most current devices support it.
WiFi 7 routers and devices are still expensive, and you need compatible devices on both ends to benefit from the new wifi technologies. Unless you need cutting-edge performance for 8K streaming or VR gaming, WiFi 6E remains a smart choice.
