WiFi speed test app runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
How Fast Is My WiFi
Looking to test how fast your Wi-Fi is? Don’t rely on online tools alone — learn smarter ways to check Wi-Fi speed and diagnose weak zones with precision.
Ways to Test Wi-Fi Speed
When people ask “how fast is my Wi-Fi?” most immediately think of online testing tools — quick services you open in a browser, press a button, and get a result. But few realize there are other ways to measure how fast your Wi-Fi really is — and some are far more accurate when it comes to identifying weak zones or capacity issues inside your network.
Let’s take a closer look at different methods of testing Wi-Fi speed — from browser-based tools to mobile apps and survey-grade diagnostics.
Online Speed Tests
When you hear the phrase “Wi-Fi speed test”, a browser-based online speed test is the fastest and most familiar option. There are many easy-to-use WiFi speed tests that can tell you everything you need to know about your wireless internet connection with the press of a single button.
Speedtest by Ookla is perhaps the most popular internet speed test service. It has been around since 2006, and it’s estimated that an unparalleled total of more than 20 billion tests have been taken with it.
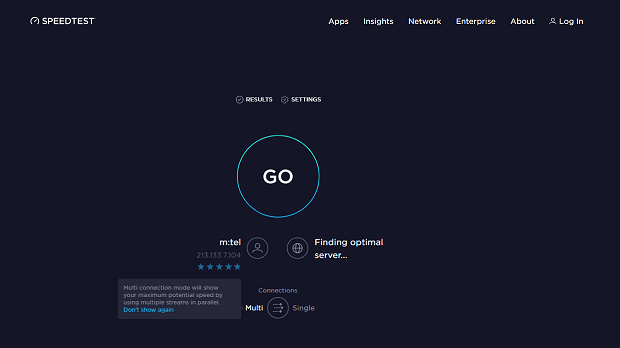
Of course, it’s not the only internet speed test service worth using. Fast.com and Speedcheck.org are both great alternatives.
Online tests are simple and convenient, but not always precise: such tests primarily capture the path from your device to a nearby server, while in-home realities like router placement, wall materials, interference from neighboring APs, or Wi-Fi congestion can skew results. Server load, ISP routing, and browser/device overhead can also introduce variance, so treat these numbers as a snapshot — not the whole story.
Mobile Apps
Mobile apps for measuring Wi-Fi speed go a step further: they let you check performance right where you actually use it.
On Android, for example, NetSpot lets you quickly check download and ping, and it automatically keeps a history of your results (including date, time, and test server).
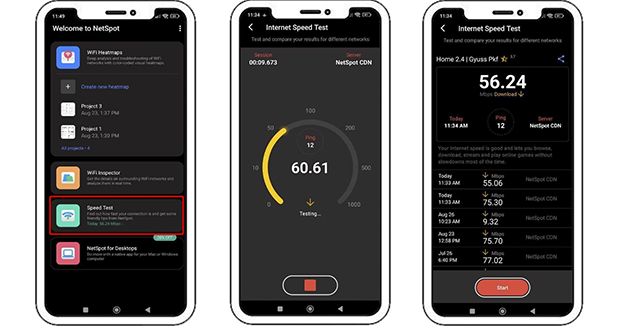
On iOS and iPadOS, NetSpot measures download, upload, and ping — and lets you ping any web or IP address right from the app. You can also ping popular websites in one tap, review the results in detail, and quickly spot latency spikes or packet loss.
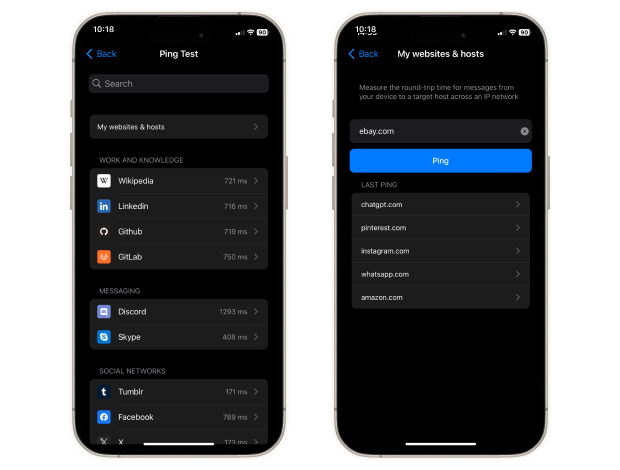
All test results are saved automatically, so you can analyze trends or spot performance drops over time.
Using more than one app (or running tests at different times of day) improves confidence in your results.
Heatmap Tools for Visualizing Wi-Fi Speed
If you want to go beyond a single speed number and truly understand how your network performs, you’ll need an app that can visualize speed across your space. Some advanced tools allow you to build Wi-Fi speed heatmaps — showing how fast your connection is in every corner of your home or office.
NetSpot’s desktop versions offer exactly that with a feature called Active Scanning. It measures download speed, upload speed, and wireless transmit rate at every data point you collect on the map. The results are turned into heatmaps that clearly show where your network performs well — and where it doesn’t.
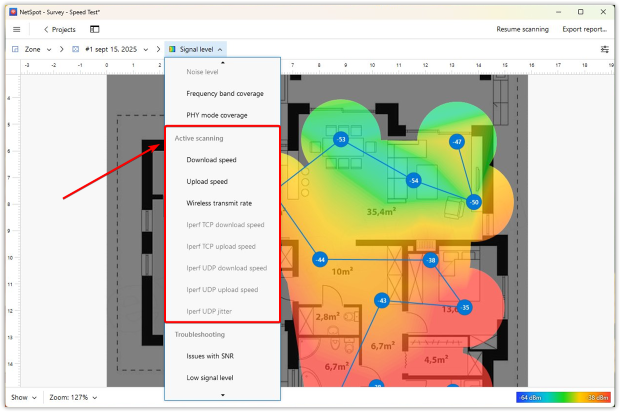
If you want to take your Wi-Fi speed analysis even further, NetSpot lets you switch between HTTP, TCP, and UDP in Active Scanning settings. Each protocol reflects a different type of network traffic: HTTP approximates web/app fetching, TCP represents most typical application traffic with congestion control, and UDP stresses real-time streams like video calls or gaming where packet timing matters more than retransmissions.
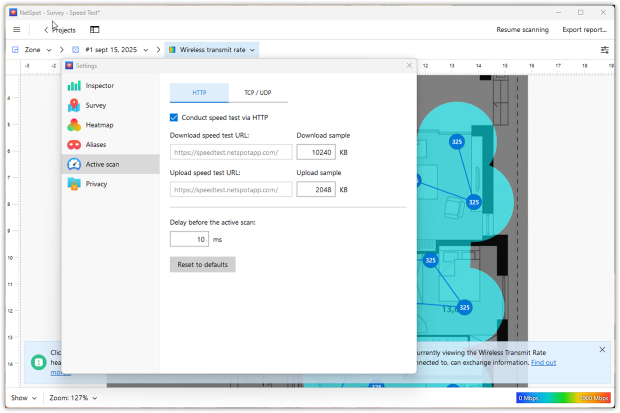
Switching protocols shows how your Wi-Fi behaves under different kinds of traffic. Professionals will also appreciate NetSpot’s integration with iPerf, enabling controlled end-to-end throughput tests between endpoints — useful for validating LAN/WLAN capacity during site surveys or troubleshooting.
After a quick online or mobile test gives you a baseline, NetSpot’s survey-grade measurements explain where and why speed changes across your floor plan — so your next optimization step is driven by data, not guesswork.
Evaluating the Results
Let’s break down what your speed test results actually mean — and how to tell whether your Wi-Fi is fast enough for the way you use it. A typical WiFi speed check result looks something like this:
- Download speed: 16.6 Mbps
- Upload speed: 5.2 Mbps
- Latency: 23 ms
Download speed refers to the speed at which you transfer data from the internet to your computer. On the other hand, upload speed refers to the speed at which data is transferred from your computer to the internet. Finally, latency is the amount of time it takes to send information from one point to the next. You can think of latency as delay. The larger it is, the more time it takes data packets to reach their destination, regardless of how fast they’re traveling.
Download and upload speed are typically measured in Mbps (Megabits per second), but some internet speed test services use MBps (Megabytes per second) instead. Because a Megabit is 1/8 as big as a Megabyte, you need a connection of 8 Mbps to download a 1 MB file in 1 second.
It also helps to separate link rate (the Wi-Fi “wireless transmit rate” your adapter shows) from throughput (what your tests measure). Link rate is a best-case physical layer speed; real throughput is lower due to protocol overhead, interference, and contention on the channel.
Rather than looking for one “perfect” number, it makes more sense to think in terms of activity-specific targets. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) recommends internet speeds of 12–25 Mbps. But if you plan on streaming Ultra HD content without bringing the connection speed of other people on the same network to a crawl, internet speeds that are closer to 100 Mbps are recommended.
Latency is measured in ms (milliseconds), and you want it to be as low as possible. For latency-sensitive tasks such as gaming or real-time video and voice communication, a latency of less than 50ms is often recommended.
Good Wi-Fi means more than just raw speed. For example:
- Gaming needs low latency and jitter
- Video calls need stable upload and low jitter
- Streaming cares about download speed and buffer
Let’s break this down using a simple table of common online activities and their recommended performance levels. These are general guidelines and may vary slightly depending on the platform, but they give a clear picture of what you should expect from your Wi-Fi.
Recommended Wi-Fi Performance Targets by Activity (2025)
| Activity | Web browsing, email |
| Download (Mbps) | 25+ |
| Upload (Mbps) | 10+ |
| Latency (ms) | ≤80 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤30 |
| Activity | HD streaming (1080p) |
| Download (Mbps) | 30-50 / stream |
| Upload (Mbps) | 10+ |
| Latency (ms) | ≤60 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤25 |
| Activity | 4K streaming (UHD) |
| Download (Mbps) | 50-100 / stream |
| Upload (Mbps) | 20+ |
| Latency (ms) | ≤60 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤20 |
| Activity | Zoom 1:1 call (1080p) |
| Download (Mbps) | 8-12 |
| Upload (Mbps) | 8-12 |
| Latency (ms) | ≤50 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤20 |
| Activity | Zoom group call (1080p) |
| Download (Mbps) | 12-20 |
| Upload (Mbps) | 12-20 |
| Latency (ms) | ≤50 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤15 |
| Activity | Cloud gaming (e.g. 1080p+) |
| Download (Mbps) | 50-75 |
| Upload (Mbps) | 25+ |
| Latency (ms) | ≤40 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤10 |
| Activity | Competitive online gaming |
| Download (Mbps) | 25-50 |
| Upload (Mbps) | 10-20 |
| Latency (ms) | ≤30 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤10 |
| Activity | Smart home, IoT devices |
| Download (Mbps) | 2–5 per device |
| Upload (Mbps) | 2+ |
| Latency (ms) | ≤100 |
| Jitter (ms) | ≤50 |
Why Is My WiFi Signal So Bad? 7 Factors That Affect WiFi Performance
WiFi can be a fickle thing. You may be enjoying a perfectly strong WiFi signal, move just a few steps in one direction, and watch it drop to one bar.
Check out a video guide on how to boost Wi-Fi signal at home — some tips and tricks as well as how to use NetSpot to see surrounding WiFi networks and perform a WiFi site survey.The seemingly unreliable nature of WiFi networks has everything to do with the fact that there are many factors that influence their performance.
- Physical distance: For obvious technical and safety reasons, WiFi routers don’t have the same transmitting power as cell towers. Cheaper routers may even struggle to cover a relatively small apartment with a strong WiFi signal — let alone an entire house. You can determine the reach of your WiFi router using a WiFi analyzer app like NetSpot.
- Obstructions: WiFi signals can be partially absorbed or even completely blocked by various obstacles and objects, including walls, duct work, furniture, home appliances, and even people. These WiFi blockers have especially negative effect on 5 GHz WiFi networks, because higher frequency signals don’t penetrate solid objects nearly as well as lower frequency signals.
- Interference: WiFi signals occupy the same radio frequency band of the electromagnetic spectrum as actual radios, cell phones, microwave ovens, walkie talkies, baby monitors, and many other devices, all of which can interfere with WiFi signals. Of course, WiFi networks can also interfere with one another, a problem that’s especially common in apartment buildings and other densely populated areas.
- Router capacity: Just like some computers can barely handle casual web browsing and some can render complex 3D objects, not all routers are equally powerful. You can’t reasonably expect a low-end router to provide reliable wireless access to the internet in a busy household or small office with dozens of active devices.
- Bandwidth hoggers: Sometimes, the problem isn’t with the strength of your WiFi signal but with the capacity of your internet connection. Video chatting or streaming on multiple devices can bring even a strong WiFi network to a crawl. For the best experience, it’s important to manage bandwidth hoggers and prevent them from stealing bandwidth from everyone else.
- Your internet service provider: You can easily waste an entire day troubleshooting poor WiFi performance without realizing that your internet service provider is actually to blame. To test if that’s really the case, connect to the internet via a wired connection and perform an internet speed test. The measured download and upload speeds should correspond to the speeds advertised by your ISP. If they don’t, then don’t hesitate to complain. If the wired baseline is solid but Wi-Fi is still slow, focus on your wireless setup instead of the ISP.
- Performance-enhancing features: Modern routers support all kinds of wonderful performance-enhancing features, including Quality of Service, Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO), beamforming, and others. However, these features may need to be manually enabled to work, and older routers often don’t support them at all. On newer gear, OFDMA, BSS coloring, and 6 GHz support can improve real-world capacity when clients support them.
Now that you understand the top 7 factors that affect WiFi performance, it’s time to take a closer look at the best devices that you can buy to give your network a quick and easy boost.
How Can I Make Wi-Fi Fast?
If you’ve just found out that you don’t exactly have a fast WiFi connection at home, don’t panic. Unlike wired internet connections, WiFi speeds fluctuate quite a lot depending on many factors, some of which are hard to control.
The distance from your WiFi router is arguably the biggest factor of them all. The farther away from it you are, the slower speeds you can expect. There are, however, multiple other factors that you need to pay attention to when trying to figure out how to get faster WiFi. Here are some tips to follow if you want fast WiFi everywhere:
- choose a better place for your router,
- get closer to your router,
- purchase a WiFi repeater,
- replace your router with a more powerful model.
We highly recommend you use NetSpot to check for dead zones, which are areas of signal weakness.
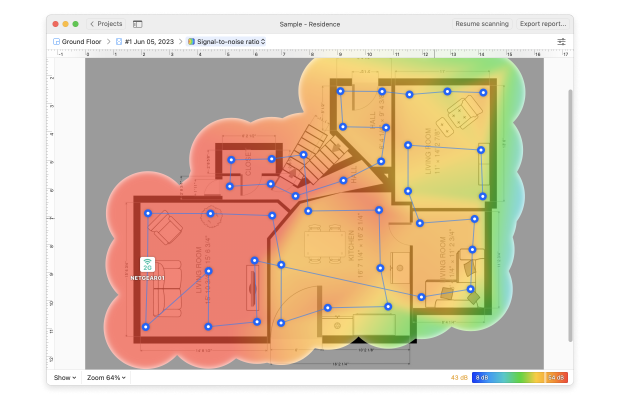
In addition to the distance separating your WiFi-enabled devices and your WiFi router, there are several other important things that can affect your home WiFi network performance that you should keep in mind as well.
Interference happens when signals outside of your WiFi network impair its operation. Such signals may come from other WiFi networks, different kinds of communication networks, and also large electronic appliances, such as your refrigerator or microwave oven. Again, choosing a good place for your WiFi router helps a lot, but you should also switch to the least cluttered WiFi channel in your area and possibly also to the 5 GHz frequency. If your devices support it, 6 GHz (Wi-Fi 6E/7) can reduce interference even more — with the trade-off of shorter range. Read How to select the best WiFi channel with NetSpot.
Last but not least, the fact that you’re not getting the speeds you’re paying for may actually have everything to do with your WiFi router.
Many older models still use outdated standards and limited bandwidth, holding back your entire network. Modern routers now support Wi‑Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Wi‑Fi 6E — offering faster speeds, better efficiency in crowded environments, and support for OFDMA, MU‑MIMO, and BSS Coloring. Early adopters are also moving to Wi‑Fi 7 (802.11be), which supports blazing-fast theoretical speeds up to 46 Gbps, wider 320 MHz channels, and extremely low latency.
If you’re still using a router with Wi‑Fi 4 (802.11n) or even Wi‑Fi 5 (802.11ac), you may not be able to take full advantage of your internet plan — especially if multiple users are streaming, gaming, or video calling at the same time.
Conclusion
The speed of your WiFi matters more than you may realize. From your laptop and smartphone to your smart TV and perhaps even your smart refrigerator, there are countless devices that require fast WiFi internet access to work properly.
The good news is that measuring how fast is your WiFi isn’t a problem thanks to many readily available internet speed test tools. As long as you know how to interpret the results and act upon them, you can make meaningful, lasting improvements. Use quick online tests for a broad check, then rely on in-place measurements and heatmaps to fix real Wi-Fi problems.
Re-survey periodically — environments change, neighbors add APs, and what worked last month might need a small tune-up today.
FAQ
Your Wi-Fi speed can be much slower than your internet plan due to local issues — not your ISP. Common causes include poor router placement, interference from other networks or devices, outdated hardware, and congestion on 2.4 GHz channels. To get full speed, make sure your router supports Wi-Fi 6 or 6E, optimize your channel settings, and check for dead zones using a Wi-Fi survey tool like NetSpot.
An internet speed test tells you how quickly your device can send and receive data from a remote server — it reflects your ISP connection, not your actual Wi-Fi performance. A Wi-Fi speed test, on the other hand, analyzes your network speed between your device and your router, showing issues like signal strength, channel overlap, and interference. Tools like NetSpot let you measure both and create heatmaps for precise diagnosis.
To test Wi-Fi speed room by room, use a mobile app or desktop software with active scanning and heatmapping features. NetSpot lets you walk through each room, capturing upload/download speed and wireless transmit rate, then visualizes the results on a heatmap. This shows exactly where your Wi-Fi signal drops or slows down — so you know where to move your router or add an access point.
Think beyond download/upload. For streaming, figure roughly 5–10 Mbps per HD stream and ~25 Mbps per 4K stream, plus headroom if several devices are active. For gaming and real-time calls, latency matters more: aim for consistently low ping (sub-50 ms is comfortable), minimal jitter, and 0% packet loss. If your online test looks great but calls still stutter, check in-room Wi-Fi with NetSpot: map Download/Upload heatmaps and watch stability (latency/jitter) where you actually sit with your laptop or phone.
Online tests primarily measure the path from your device through your ISP to a remote server. Server distance, routing, congestion, browser overhead, VPNs, and even which band your device picked (2.4/5/6 GHz) can move the numbers up or down. For the fairest comparison, test multiple services, repeat at different times, and note band and channel width. For Wi-Fi-specific truth, pair those with in-place tests and Survey heatmaps in NetSpot so you see what your wireless can actually deliver room by room.
If your wired Ethernet test matches your plan but Wi-Fi is slower or unstable, the bottleneck is wireless: channel overlap, channel width, placement, or capacity. If both wired and Wi-Fi underperform, call the ISP. To be sure, compare three snapshots: wired baseline at the router, Wi-Fi next to the router, and Wi-Fi in the problem room. Use NetSpot’s Survey Mode to visualize weak zones and Active Scanning to validate fixes after you change channels, move the AP, or add a mesh node.

