Enquêtes de site Wi-Fi, analyse, dépannage fonctionnent sur un MacBook (macOS 11+) ou tout ordinateur portable (Windows 7/8/10/11) avec un adaptateur réseau sans fil standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b. En savoir plus sur la prise en charge du 802.11be ici.
Qu'est-ce que le WiFi 6E et dois-je passer à cette technologie ?
Les normes WiFi évoluent constamment pour répondre à nos besoins croissants en connectivité. Le WiFi 6E, introduit en 2020, a apporté des améliorations significatives aux réseaux locaux sans fil en ouvrant pour la première fois la bande 6 GHz.
Bien que n'étant plus la norme WiFi la plus récente, le WiFi 6E reste pertinent et mérite d'être envisagé si vous souhaitez des améliorations en termes de vitesse, de couverture et de fiabilité.
Qu'est-ce que le Wi-Fi 6E ?
WiFi 6E est le terme marketing utilisé pour désigner la norme IEEE 802.11ax pour les réseaux locaux sans fil. Le WiFi 6E est arrivé en 2020, juste un an après l'introduction du WiFi 6, qui est également basé sur la norme IEEE 802.11ax.
Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E
La principale différence entre le WiFi 6 et le WiFi 6E réside dans le fait que la dernière génération WiFi prend en charge trois différentes bandes de fréquences (2,4 GHz, 5 GHz et 6 GHz), alors que la première ne prend en charge que deux (2,4 GHz, 5 GHz).
La prise en charge de la bande des 6 GHz est très importante si vous vivez dans une zone où il y a plus de réseaux WiFi que d'arbres. Dans de telles zones, les interférences sans fil tendent à être un problème majeur, causant des fluctuations imprévisibles des vitesses pour tout le monde et rendant difficile l’obtention d’une couverture signal uniforme.
Dans la bande des 6 GHz, il y a 59 canaux supplémentaires de 20 MHz et 29 canaux supplémentaires de 40 MHz, et c'est grâce à eux que les vitesses du WiFi 6E peuvent largement dépasser celles du WiFi 6. C'est pourquoi le WiFi 6E est également connu sous le nom de Wi-Fi à Haute Efficacité.
| WiFi 6 | WiFi 6E | |
|---|---|---|
| Introduit | 2019 | 2020 |
| Norme IEEE | 802.11ax | 802.11ax |
| Débit de liaison maximal (Mbit/s) | 600 à 9608 | 600 à 9608 |
| Bandes prises en charge | 2.4/5 | 2.4/5/6 |
Quels sont les avantages du Wi-Fi 6E ?
Nous avons déjà abordé certains des principaux avantages du WiFi 6E, et il est maintenant temps de les examiner de plus près :
- Vitesse : Tandis que le WiFi 6 et le WiFi 6E peuvent théoriquement atteindre le même taux de liaison maximal, les routeurs et appareils WiFi 6 ne peuvent pas profiter de la bande des 6 GHz pour éviter les ralentissements liés aux interférences. C'est pourquoi le WiFi 6E l'emporte presque toujours en termes de vitesses réelles.
- Couverture : Parce que les routeurs WiFi 6E et les systèmes mesh WiFi 6E peuvent utiliser trois différentes bandes de fréquence, il est beaucoup plus facile d'obtenir une excellente couverture du signal même dans les zones urbaines densément peuplées.
- Fiabilité : La fiabilité de tout réseau WiFi va de pair avec sa vitesse et sa couverture. Comme les réseaux WiFi 6E sont plus rapides que ceux qui reposent sur les normes WiFi précédentes, il est beaucoup moins probable de voir votre vitesse chuter en dessous d'un niveau acceptable. De même, les réseaux WiFi 6E peuvent couvrir une zone plus étendue avec un signal fort, donc votre connexion ne chutera pas simplement parce que vous faites quelques pas de plus avec votre smartphone ou ordinateur portable dans la mauvaise direction.
- Sécurité : Tous les appareils WiFi 6E soutiennent la dernière norme WiFi en matière de sécurité, l'Accès Protégé Wi-Fi 3 (WPA3). La nouvelle norme WiFi est rétrocompatible avec WPA2 et elle traite les problèmes de sécurité posés par les mots de passe faibles et les réseaux publics.
Ces avantages rendent la mise à niveau vers le WiFi 6E valable tant pour l'effort que pour l'investissement financier nécessaire. Cependant, ne pensez pas que le WiFi 6E puisse résoudre les problèmes causés par un mauvais placement ou une mauvaise configuration du routeur. Oui, la meilleure performance des appareils WiFi 6E peut les rendre moins apparents, mais elle ne les fera pas disparaître.
Pour les résoudre, nous recommandons l'utilisation d'un outil d'analyse de réseau WiFi comme NetSpot.
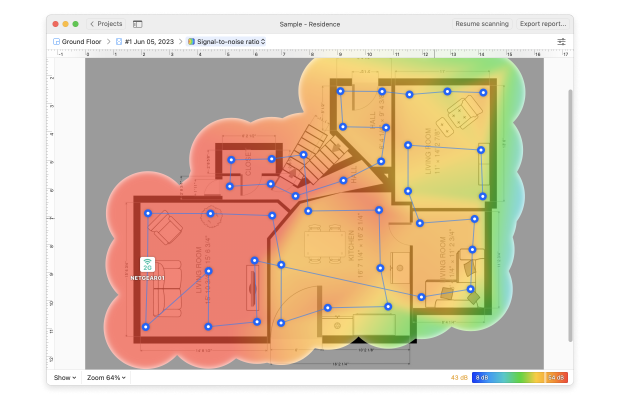
Avec son aide, vous pouvez créer une carte de couverture détaillée pour déterminer si votre routeur est situé à l'endroit optimal, et vous pouvez également découvrir tous les réseaux WiFi à proximité et voir si leur configuration n'entre pas en conflit avec la configuration de votre propre réseau.
Quels sont les inconvénients du WiFi 6E ?
Le WiFi 6E apporte des améliorations significatives par rapport à ses prédécesseurs, incluant des débits de données plus élevés, une capacité accrue, une latence réduite, et une couverture élargie dans la bande des 6 GHz. Cependant, comme toute technologie, il a ses inconvénients. Voici certains des principaux désavantages :
- Compatibilité limitée avec les appareils : À la date de ma dernière mise à jour, tous les appareils ne supportent pas le WiFi 6E. Les appareils plus anciens pourraient ne pas pouvoir se connecter aux réseaux WiFi 6E, nécessitant ainsi des routeurs bi-bande ou tri-bande offrant également des réseaux à 2,4 GHz et 5 GHz pour la compatibilité. Cette situation va s'améliorer au fur et à mesure que plus de nouveaux appareils seront fabriqués avec le support du WiFi 6E.
- Coût : Les routeurs et appareils WiFi 6E ont tendance à être plus chers que leurs équivalents WiFi 5 (802.11ac) et WiFi 6 (802.11ax). Le prix élevé reflète la nouvelle technologie et les caractéristiques améliorées, rendant l'adoption initiale plus coûteuse pour les consommateurs et entreprises.
- Disponibilité limitée de la bande des 6 GHz dans le monde : La disponibilité de la bande des 6 GHz, cruciale pour le WiFi 6E, varie selon les pays. Une approbation réglementaire est nécessaire, et tous les pays n'ont pas ouvert ce spectre pour l'utilisation du WiFi. Cette limitation affecte le taux d'adoption mondial et l'efficacité du WiFi 6E à offrir ses pleins bénéfices partout.
- Potentiel d'interférence dans les environnements denses : Bien que la bande des 6 GHz soit moins encombrée que celles de 2,4 GHz et 5 GHz, il y a un potentiel d'interférence dans les zones densément peuplées ou dans des environnements avec nombreux appareils à 6 GHz. À mesure que l'adoption augmentera, la gestion de cette congestion sera importante pour maintenir la haute performance attendue du WiFi 6E.
- Consommation d'énergie accrue : Les caractéristiques avancées du WiFi 6E, telles que le débit et la capacité supérieurs, peuvent conduire à une consommation d'énergie accrue sur les appareils. Cela peut impacter la durée de vie de la batterie, en particulier sur les appareils mobiles et les applications IoT, nécessitant des charges plus fréquentes ou des batteries plus grandes.
- Limitations de portée en intérieur : Les signaux à 6 GHz utilisés par le WiFi 6E ont une portée plus courte et sont moins efficaces pour pénétrer les objets solides comme les murs et les planchers comparativement aux signaux de 2,4 GHz. Cela pourrait nécessiter l'utilisation de plus de points d'accès ou de systèmes maillés pour assurer une couverture complète dans les maisons ou bâtiments plus grands.
Bien que le WiFi 6E présente ces inconvénients, ses avantages pour les environnements à forte demande et la pérennité des réseaux l'emportent souvent sur les points négatifs pour de nombreux utilisateurs. À mesure que l'écosystème mûrit, les coûts vont probablement diminuer et la compatibilité des appareils s'élargira, atténuant certains de ces inconvénients.
Routeurs WiFi 6E et Systèmes maillés
Choisir le meilleur routeur ou système mesh WiFi 6E peut être un processus long et déroutant. Pour vous faciliter la tâche, nous avons compilé la liste suivante de nos options préférées.
Routeurs WiFi 6E
Les meilleurs routeurs WiFi 6E continuent d'offrir d'excellentes performances pour ceux qui souhaitent profiter de la bande 6 GHz sans passer tout de suite au WiFi 7. Voici nos meilleurs choix :
- ASUS RT-AXE7800 — Ce routeur gaming WiFi 6E tri-bande offre une capacité de vitesse de 7800 Mbps, un port Internet multi-gig, un processeur quad-core et un espace de stockage conséquent. Les fonctionnalités incluent la sécurité AiProtection Pro, le VPN Instant Guard, des contrôles parentaux avancés et la compatibilité ASUS AiMesh pour étendre la couverture dans toute la maison.
- Netgear Nighthawk RAXE500 — Un routeur Wi-Fi 6E tri-bande au design élégant avec un port WAN 2,5 Gbps pour l’internet multi-gig, ainsi que quatre ports LAN gigabit et deux ports USB. Propulsé par un processeur quad-core 1,8 GHz, il offre des vitesses WiFi exceptionnelles jusqu’à 10,8 Gbps et couvre jusqu’à 325 mètres carrés pour 60 appareils.
- TP-Link Archer AXE75 — En termes de rapport qualité-prix et de performance, le TP-Link Archer AXE75 est l’un des meilleurs routeurs Wi-Fi 6E disponibles. Il offre des vitesses ultra-rapides sur la bande 6 GHz tout en maintenant de faibles latences car il est équipé d’un CPU quad-core de 1,7 GHz, de 512 Mo de mémoire et d’une prise en charge VPN complète (OpenVPN/PPTP/L2TP).
Systèmes Mesh WiFi 6E
Nos meilleurs systèmes mesh WiFi 6E continuent d’offrir une excellente couverture complète de la maison avec les avantages de la bande 6 GHz :
- Netgear Orbi RBKE963 — Ce système quadri-bande offre le premier support quadri-bande de l'industrie pour fournir des vitesses fulgurantes jusqu'à 10,8 Gbps et une couverture jusqu'à 840 mètres carrés. Bien qu’il soit cher (environ 1 500 $ pour un pack de trois appareils), il est garanti que vous n'aurez pas à changer de système WiFi avant longtemps.
- TP-Link Deco XE75 — Le Deco XE75 offre des vitesses impressionnantes pour un système mesh, en partie grâce à la ligne dédiée Deco-à-Deco. Il propose également des contrôles parentaux basiques et des outils VPN intégrés qui éliminent le besoin de produits tiers. Sa couverture atteint 670 mètres carrés avec trois unités et 510 mètres carrés avec deux unités.
- eero Pro 6E — L’eero Pro 6E est un autre excellent système mesh Wi-Fi 6E compatible avec la bande 6 GHz. Il offre des vitesses de téléchargement de 1,44 Gbps à courte distance et inclut un port Ethernet 2,5 Gbps pour l’internet multi-gig. Vous pouvez également l’acquérir avec l’abonnement eero Plus, qui vous donne accès à tout, des contrôles parentaux à la protection contre les logiciels malveillants en passant par le blocage des publicités.
Comment le WiFi 6E se compare-t-il au WiFi 7 ?
| WiFi 6E | WiFi 7 | |
|---|---|---|
| Norme IEEE | 802.11ax | 802.11be |
| Date de sortie | 2020 | 2024 |
| Débit théorique maximal | 9,6 Gbps | 46 Gbps |
| Bandes de fréquences | 2,4/5/6 GHz | 2,4/5/6 GHz |
| Largeur de canal maximale | 160 MHz | 320 MHz |
| QAM | 1024-QAM | 4096-QAM |
| Opération Multi-Lien | Non | Oui |
| Fonctionnalités principales | Bande 6 GHz, OFDMA, Target Wake Time | MLO, Multi-RU, Transmission Poinçonnée |
WiFi 7 (802.11be), officiellement lancé début 2024, est la toute dernière norme WiFi et le successeur direct du WiFi 6E. Également connu sous le nom de IEEE 802.11be Extremely High Throughput (EHT), il améliore de façon spectaculaire la vitesse, l’efficacité et la fiabilité.
L’avancée la plus remarquable du WiFi 7 est l’Opération Multi-Lien (MLO), qui permet aux appareils de se connecter simultanément sur plusieurs bandes et canaux. Cela signifie que votre appareil peut utiliser les bandes 2,4 GHz, 5 GHz et 6 GHz en même temps pour des performances optimales. Le WiFi 7 double également la largeur de canal à 320 MHz (contre 160 MHz pour le WiFi 6E), introduit la modulation 4K-QAM permettant des taux de transmission 20 % plus élevés, et met en œuvre des fonctionnalités avancées telles que l’allocation Multi-Resource Unit (MRU) et la transmission ponctuelle pour maximiser l’efficacité.
La vitesse maximale théorique du WiFi 7 atteint un impressionnant 46 Gbit/s — soit près de cinq fois plus rapide que les 9,6 Gbit/s du WiFi 6E. En conditions réelles, le WiFi 7 peut offrir des vitesses dépassant 5 Gbit/s pour chaque appareil, ce qui le rend idéal pour les applications gourmandes en bande passante comme le streaming 8K, les jeux VR/AR et les transferts de fichiers volumineux.
Cependant, il est important de noter que les routeurs et appareils compatibles WiFi 7 restent relativement onéreux, et que pour profiter pleinement de cette nouvelle technologie, il faut des équipements compatibles des deux côtés. Pour la plupart des utilisateurs actuellement, le WiFi 6E demeure un excellent choix qui offre des améliorations substantielles par rapport aux anciennes normes à un tarif plus accessible.
Bon à savoir : NetSpot pour Windows prend déjà en charge le WiFi 7, ainsi que le WiFi 6E et toutes les normes précédentes.
Conclusione
Le WiFi 6E étend le réseau sans fil à la bande des 6 GHz pour la première fois, offrant ainsi des vitesses plus rapides, moins d’interférences et de meilleures performances pour les appareils compatibles. Les routeurs et systèmes maillés WiFi 6E recommandés dans cet article offrent un excellent rapport qualité-prix et performances, et constituent un choix judicieux, même alors que la nouvelle norme WiFi, le WiFi 7, devient de plus en plus disponible, grâce à leur excellent rapport prix-performances.
WiFi 6E — FAQ
WiFi 6E est le terme marketing utilisé pour désigner la norme IEEE 802.11ax pour les réseaux locaux sans fil.
Le WiFi 6E peut tirer parti de trois différentes bandes de fréquences (2,4 GHz, 5 GHz et 6 GHz), tandis que le WiFi 6 n'en supporte que deux (2,4 GHz, 5 GHz). Grâce à la bande supplémentaire, le WiFi 6E offre de meilleures performances que le WiFi 6.
Bien que le WiFi 6 et le WiFi 6E puissent théoriquement atteindre le même débit maximal en lien, le WiFi 6E peut être jusqu'à 25 pour cent plus rapide dans le monde réel car il prend en charge la bande des 6 GHz.
Non, les appareils qui ne supportent que le WiFi 6 ne peuvent pas utiliser le WiFi 6E. En même temps, tous les routeurs et systèmes maillés WiFi 6E sont rétrocompatibles avec le WiFi 6, donc ils peuvent connecter sans problème les clients uniquement WiFi 6 à Internet.
Oui, il existe de nombreux excellents systèmes mesh WiFi 6E disponibles. Les meilleures options incluent le Netgear Orbi RBKE963, qui offre une prise en charge quadri-bande, le TP-Link Deco XE75, qui offre un excellent rapport qualité-prix avec des vitesses allant jusqu'à 5 400 Mbps, et l'eero Pro 6E, qui dispose d'un port Ethernet de 2,5 Gbps.
Si vous n'êtes pas satisfait des performances de votre réseau WiFi et que vous avez optimisé sa configuration et sa couverture à l'aide d'un analyseur de réseau comme NetSpot, alors un routeur WiFi 6E pourrait être un excellent investissement.
Le Netgear Nighthawk RAXE500 est le routeur WiFi 6E le plus rapide car il offre des vitesses WiFi combinées exceptionnelles de 10,8 Gbps grâce à son processeur quad-core de 1,8 GHz. Un autre modèle très rapide est l’ASUS RT-AXE7800, qui propose des vitesses impressionnantes à un tarif plus abordable.
Non, le WiFi 7 est nettement plus rapide que le WiFi 6E. Alors que le WiFi 6E offre une vitesse maximale théorique de 9,6 Gbps, le WiFi 7 (802.11be) peut atteindre jusqu'à 46 Gbps en théorie, soit près de cinq fois plus rapide. Le WiFi 7 introduit également l’Opération Multi-Liaison (MLO), qui permet aux appareils d’utiliser plusieurs bandes simultanément. Par conséquent, vous êtes moins susceptible de subir des baisses soudaines de performances dues à des interférences de signal.
Le WiFi 7 est techniquement supérieur au WiFi 6E, offrant des vitesses plus élevées, une latence plus faible et des fonctionnalités avancées comme MLO et les canaux de 320 MHz. Cependant, « meilleur » dépend de vos besoins spécifiques. Pour la plupart des utilisateurs en 2025, le WiFi 6E offre un meilleur rapport qualité-prix car il propose d'excellentes performances à un prix plus accessible, et la plupart des appareils actuels le prennent en charge.
Les routeurs et appareils WiFi 7 restent chers, et il faut des appareils compatibles des deux côtés pour bénéficier des nouvelles technologies wifi. À moins que vous n'ayez besoin de performances de pointe pour le streaming 8K ou les jeux VR, le WiFi 6E reste un choix judicieux.
