Wi-Fi 站点调查、分析、故障排除 运行在 MacBook (macOS 11+) 或任何带有标准 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b 无线网络适配器的笔记本电脑 (Windows 7/8/10/11) 上。相关 802.11be 支持的详细信息请点击 这里。
现在,房主与客人分享他们家中WiFi密码已经成为一种常见做法。然而,这种做法存在严重的安全隐患。毕竟,你不会给每一个来到你家的客人都配一把自己的钥匙,对吧?当然,你也不希望朋友和家人在拜访你时为了提升安全性而无法上网。解决办法是什么?访客WiFi网络!
什么是访客 Wi-Fi 网络?
访客WiFi网络基本上是一个次要网络,专门供访客和其他临时用户使用。
面向公众的企业通常会创建访客无线网络,以便为客户提供互联网接入,而无需让他们连接到企业服务器、计算机和其他IT资产所在的同一网络。
普通家庭用户也可以创建访客网络,而且大多数现代路由器使这一过程非常简单。以这种方式使用时,访客网络可以防止访客访问诸如打印机、网络附加存储和共享文件夹等共享网络资源。
为了达到预期目的,在配置WiFi加密和安全设置时,通常会使用独特的密码来保护访客网络,而不是重复使用保护主网络的密码。
为何要设置访客Wi-Fi网络?
即使你不介意与他人分享你的 WiFi 密码,创建一个访客 WiFi 网络也有很多充分的理由。让我们来探讨其中的一些原因:
- 增强安全性:许多介绍如何阻止 WiFi 黑客的指南通常建议用户创建访客 WiFi 热点,将设备隔离,作为防止窥探的预防措施。当访客设备在他们自己的网络中时,任何感染这些设备的恶意软件都不容易传播到同一网络中的其他设备;但如果它们被分开在各自的网络中,这种传播就无法发生,这也是访客 WiFi 网络可以提升你安全性的额外方式。
- 带宽提升:你的路由器能提供的带宽是有限的,所以与访客完全共享带宽并不是个好主意,尤其是当你经常需要进行高带宽任务,如视频会议或运行家庭服务器时。高性能路由器允许你限制访客可用的带宽,甚至可以为你自己的设备保留一个完整的 WiFi 频段。
- 便利性:即使你不在意安全或性能,运行访客 WiFi 网络所带来的便利性也很难被忽视。例如,你可以将访客网络的密码打印在一张纸上并装裱,然后像独特又实用的装饰品一样挂在墙上,一定能成为打破冷场的好帮手。
- 成本:访客 WiFi 网络的另一个好处是它们的创建不需要任何成本。大多数路由器—不仅仅是高端型号—都直接支持此功能,通常只需点击一下即可启用,这当然比为了访客再买一个路由器要划算得多。
- 灵活性:只因为你开启了访客 WiFi 网络一次,并不代表你必须一直保持开启。你可以轻松将其关闭—无论是暂时还永久。你的主 WiFi 网络不会受到任何影响。
正如你所看到的,学习如何设置访客 WiFi 网络能够带来许多宝贵的好处,本文下一部分将一步步为你详细说明具体操作流程。
如何设置访客 Wi-Fi 网络
按照以下步骤设置访客WiFi网络:
打开你的路由器管理面板。现在的路由器通常配有手机应用,让设置变得简单。较老的路由器可以通过网页管理面板进行管理,只需在网页浏览器中输入路由器的IP地址即可(常用地址包括192.168.1.1、192.168.0.1和10.0.1.1)
以管理员身份登录到管理面板。要启用访客WiFi网络,您可能需要输入管理员用户名和密码。如果您不记得更改过这些信息,可以尝试“admin/admin”因为这些是最常见的默认管理员登录凭据。
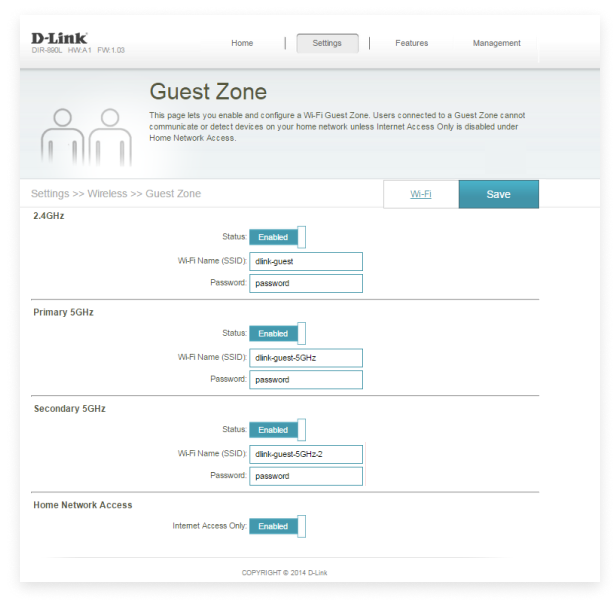
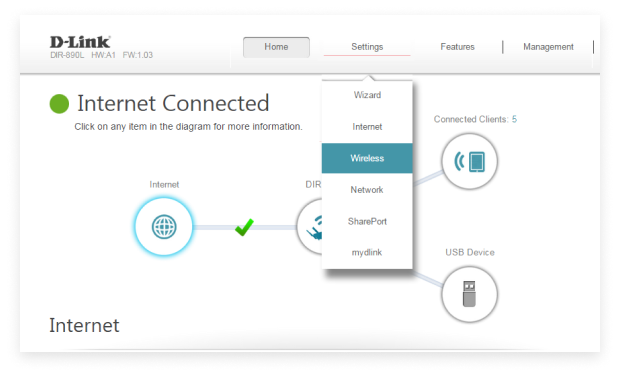
找到访客WiFi设置。该设置的具体位置取决于您的路由器品牌和型号,但您可以在无线设置菜单和额外功能菜单等位置查找。
启用访客WiFi选项。在大多数情况下,您只需点击相应的复选框或按钮即可。
NetSpot 可以收集您实际区域内所有 WiFi 网络的详细信息,并在地图上可视化覆盖范围,以显示所有信号死区等信息。
您的路由器可以创建访客网络吗?
虽然访客 WiFi 功能越来越常见,但仍有一些路由器不支持该功能。要了解您的路由器是否可以创建访客网络:
准确找出你拥有的是哪一款路由器。相关信息应写在路由器上某处的标签上。

在其制造商网站上查找该路由器。大多数制造商会将访客 WiFi 功能作为一个有用的额外功能进行宣传。

如果您仍然不确定该路由器是否可以创建访客WiFi,请直接联系制造商。

请注意,并非所有制造商都将访客WiFi功能称为同一个名称。例如,D-Link称其为“访客专区”
访客无线网络可以阻止物联网威胁
正如我们此前在本文中解释过的,访客 WiFi 的安全性优势来自于访客 WiFi 在访客和主网络设备之间所创建的隔离。
这种隔离同样可以用来阻止物联网(IoT)威胁,如黑客攻击和恶意软件。这样,你就无需因为不信任你的智能家居设备像制造商声称的那样安全而不断自问:"谁在连接我的 WiFi?"物联网安全的现实可能令人担忧)。
相反,你可以放心,因为即使是最有技术的黑客也无法从你的访客网络跳转到主网络,从而入侵你的个人设备。
常见问题解答:访客 WiFi 网络详解
访客网络是专为访客创建的独立AP,防止他们访问您的主网络。它有自己的密码,通常有诸多限制,这样通过隔离可立即提升安全性。因此,在设置家庭WiFi时,您应从基础的安全措施和独立的SSID开始。
即使完全信任他人,访客网络也能防止他人的手机或笔记本电脑意外感染恶意软件,同时还意味着你不需要与他人共享网速—你的视频通话和下载速度不会变慢。这在有许多设备的繁忙家庭中尤为重要。在部署家庭WiFi网络时,应将这一点考虑在内。
大多数现代路由器都默认支持访客网络,但为确认这一点,请检查您设备上的型号标签,并在制造商网站上查询有关“访客访问”或类似术语(例如,D-Link 称之为“访客专区”的功能信息。如果未列出此功能,请联系支持部门。在部署 Wi-Fi时,此功能尤为重要,而且无需额外成本。它在不影响主连接的情况下,提供了灵活性。
登录到您的路由器管理面板(通过IP或应用程序)找到访客网络部分,启用它,创建一个单独的SSID和强密码,并在必要时限制带宽。就这样 — 您的网络已经准备就绪,客人可以连接而不会危及您的设备。当您的设备数量较多时,考虑带宽非常重要,以确保没有人占用过多信道—这在WiFi 容量的文章中有详细介绍。
是的,正是因为隔离:即使黑客入侵了访客网络上的智能灯泡或摄像头,他们也无法“跳转”到你的电脑、手机或NAS上。这是构建可靠无线基础设施的基本技术之一,其中VLAN和流量分割起着关键作用,这在无线基础设施概述中已经讨论过。
理想的做法是:只在活动期间开启网络,醒目地公布密码,所有内容都在线上,无须任何问题。面对大量人群时,这有助于管理负载并防止超载,这在类似于临时高密度活动网络的拥挤场景中尤为重要。