Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
RF (Radio Frequency) Site Survey
A radio frequency site survey (or just RF site survey) can help overcome this challenge by providing vital information about the behavior of radio waves within the covered area.
It can be a real challenge to design a wireless network that covers a large area with a strong signal without dead zones or overuse of networking equipment.
What Is RF Site Survey and What Is It for?
An RF site survey is the process of determining the optimal configuration of a wireless network and placement of wireless access points to provide adequate signal coverage (a minimum data rate or throughput) throughout a certain area.
Typically, RF site survey software tools such as NetSpot are used to visualize signal coverage on a map and highlight all places where the coverage isn’t adequate.
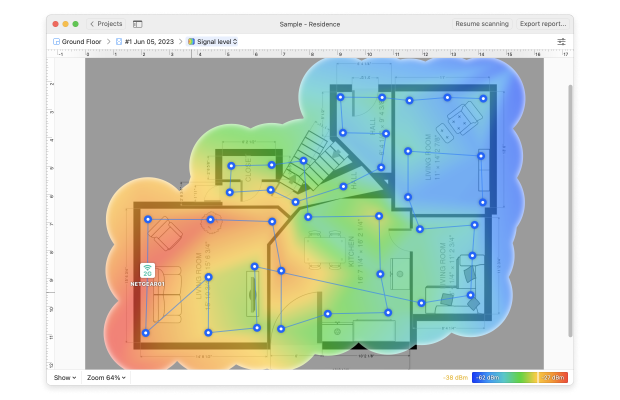
RF site survey tools greatly simplify this otherwise complex process, making it possible for virtually anyone to discover a problem with the propagation of radio waves and the presence of interfering signals without specialized hardware equipment.
Over the past several years, the ability to connect wireless to the internet has become more important than ever, and the same is true for RF site surveys. Businesses use them to cover multi-store office builds and support employee mobility, brick-and-mortar stores rely on them to offer their customers problem-free access to the internet, and individual home users conduct radio frequency site surveys to get the most out of their internet connection.
What Are the Steps in Conducting an RF Site Survey?
When conducting an RF site survey, there are certain general steps that should be taken every time to ensure the best results possible.
Obtain Supporting Documentation
Before you launch your RF site survey tool of choice, you should obtain as much supporting documentation about the surveyed area as possible. If nothing else, make sure to get a map or diagram of the area. When surveying a larger facility, your best bet is the official construction blueprint. It’s also useful to have some information about the materials used during the construction and about other sources of radio requency emissions in the area.Inspect the Surveyed Area
The role of documentation in an RF site survey is to provide supporting information and help you complete the RF site survey process and optimize the wireless network to achieve the best performance and coverage possible.
However, documentation alone doesn’t tell the full story. A simply physical inspection can quickly reveal obstacles to wireless signals that blueprints rarely show, such as large metal appliances. Without being familiar with the presence of various obstacles to wireless signals, it would be very difficult to accurately interpret the results of the RF site survey and take suitable corrective actions.
Evaluate the Existing Network Infrastructure
Does the area you want to cover with a strong wireless signal have an existing Ethernet or optical network? How many wireless routers are currently present? Does each router broadcast a different wireless network or is the area covered with a mesh network? These are just some of the questions you should be asking in regard to the existing network infrastructure to know exactly what will need to be done later on.Identify Usage Patterns
Unless we’re talking about a very small area, such as a family house, apartment building, or a single office, the chances are that you won’t need to cover every single square inch with a strong wireless signal. To lower your equipment costs and accelerate the RF site survey process, you should identify usage patterns and key coverage areas.
Do you need coverage in bathrooms, break rooms, and parking garages? What about elevators? By answering these important questions upfront, you will know exactly how to interpret the results of your RF site survey and provide adequate signal coverage without wasting time, money, and energy on goals that are unlikely to make any practical impact.
Conduct the RF Site Survey
Now it’s time to conduct the RF site survey using an RF site survey tool like NetSpot (more about NetSpot in the next section of this article). Your RF site survey tool should guide you through the entire process and tell you exactly which areas you need to survey. When conducting the RF site survey, take your time and don’t rush things. Keep your measurements as consistent as possible by following the same steps for each individual measurement.
Interpret the Results and Make Changes
With the right RF site survey tool, you won’t have to do much to interpret the results of your survey because the tool will automatically highlight all areas of signal weakness and help you discover problems such as cross-channel interference. All you need to do is make changes to the wireless network to improve its performance, such as replacing the existing wireless router with a more powerful one or using a signal booster to extend the signal.
Ongoing Monitoring
After you make changes to improve the performance of the surveyed wireless network, you should continue monitoring it on an ongoing basis. You may discover that the performance of the network fluctuates over time, which would warrant an additional RF site survey to be performed. Make sure to document everything so you can always go back and compare current results with past results.
NetSpot for RF Site Survey
NetSpot is a versatile and easy to use RF site survey tool that provides its users with a comprehensive and complete RF site survey solution that can be used by professionals and home users alike.
Despite being one of the most accessible tools in its category, NetSpot delivers highly accurate results and offers multiple visualizations to instantly uncover all problems with wireless networks.
In addition to its powerful RF site survey capabilities, NetSpot can also collect every detail about surrounding wireless networks and present the gathered data, such as signal level, interference, noise, etc., as an interactive table.
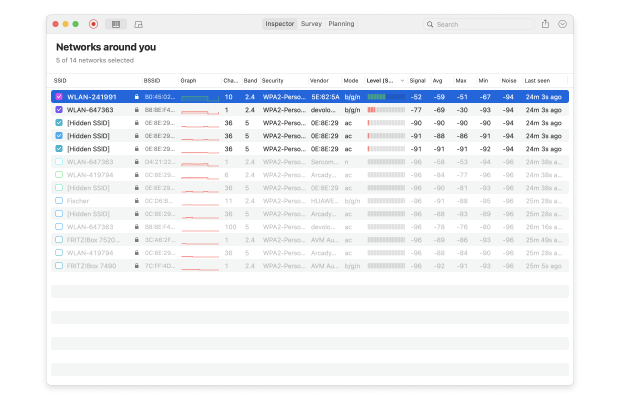
NetSpot is compatible with both Mac and Windows, and it supports 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz frequency bands at 20/40/80/160 MHz channels.
RF (Radio Frequency) Site Survey — FAQs
An RF (Radio Frequency) survey is a process used to analyze and evaluate the RF environment, including signal strength, interference, and coverage areas, to optimize the performance and placement of wireless networks and devices.
To conduct an RF site survey, you typically use specialized tools to measure signal strength, identify interference sources, and map out coverage areas, followed by analyzing this data to plan the placement of wireless access points for optimal network performance and coverage. One of the versatile RF site survey tools is NetSpot.
The three types of wireless site surveys are passive surveys, where devices listen to the environment without transmitting; active surveys, which involve measuring network performance by connecting to access points; and predictive surveys, which use software simulations to model wireless coverage in a virtual environment.
The purpose of a wireless site survey is to ensure optimal placement of access points and identify the best configuration for a wireless network to provide comprehensive coverage and high performance, while minimizing interference and signal loss.
